

- Home
- Companies
- Earth Shield Environmental Co., Ltd.
- Articles
- How to use Geotube?

How to use Geotube?
Geotubes are multi-functional and play a crucial role in various coastal engineering and environmental management applications. In the realm of coastal protection, they are widely utilized for erosion control. Whether it’s in the construction of revetments, dykes, groynes, or breakwaters, geotubes act as effective barriers. By being strategically placed along the shoreline, they can reduce the erosive impact of waves and currents, safeguarding the coastline and protecting adjacent properties like hotels and beachfront homes.
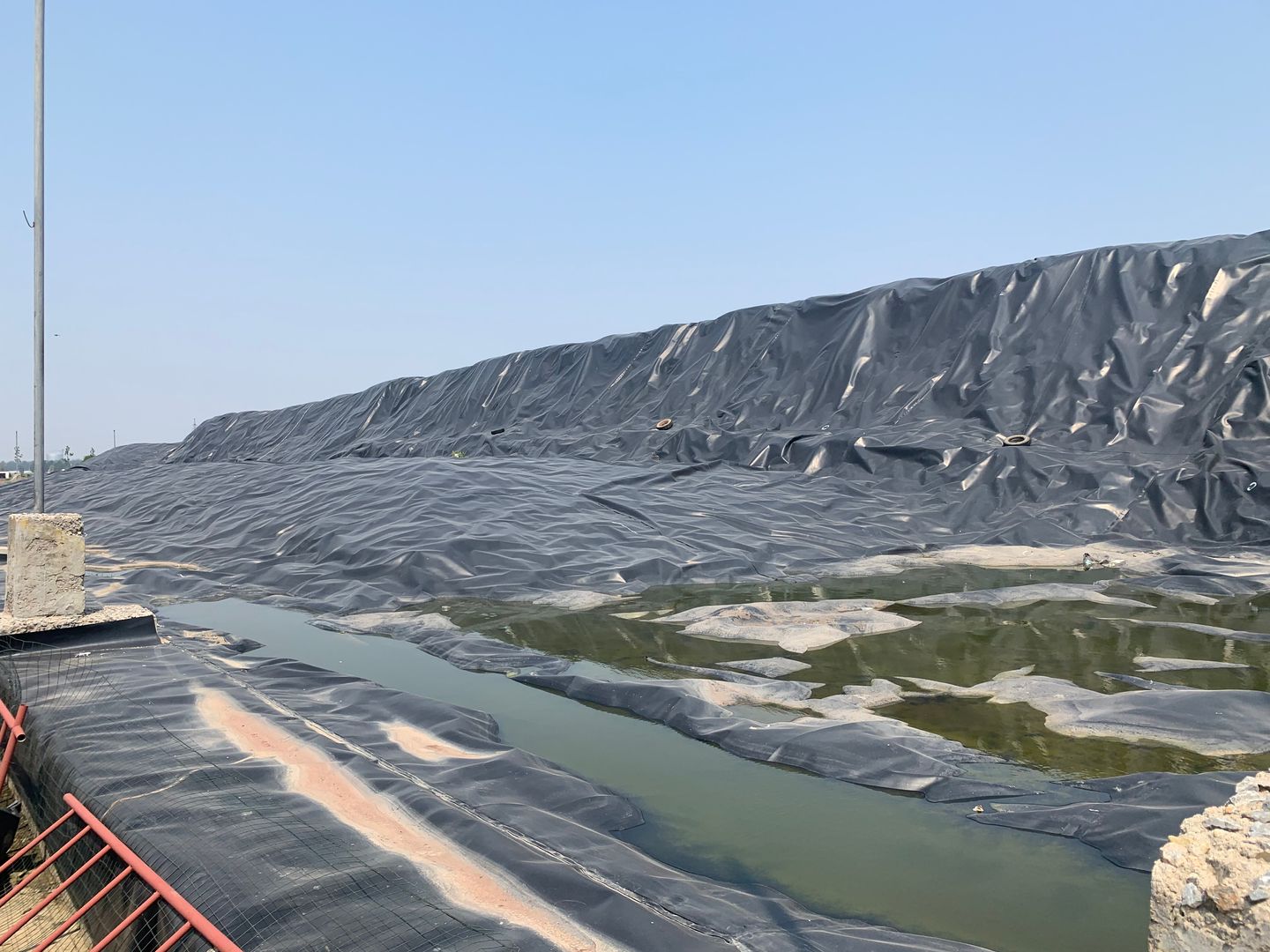
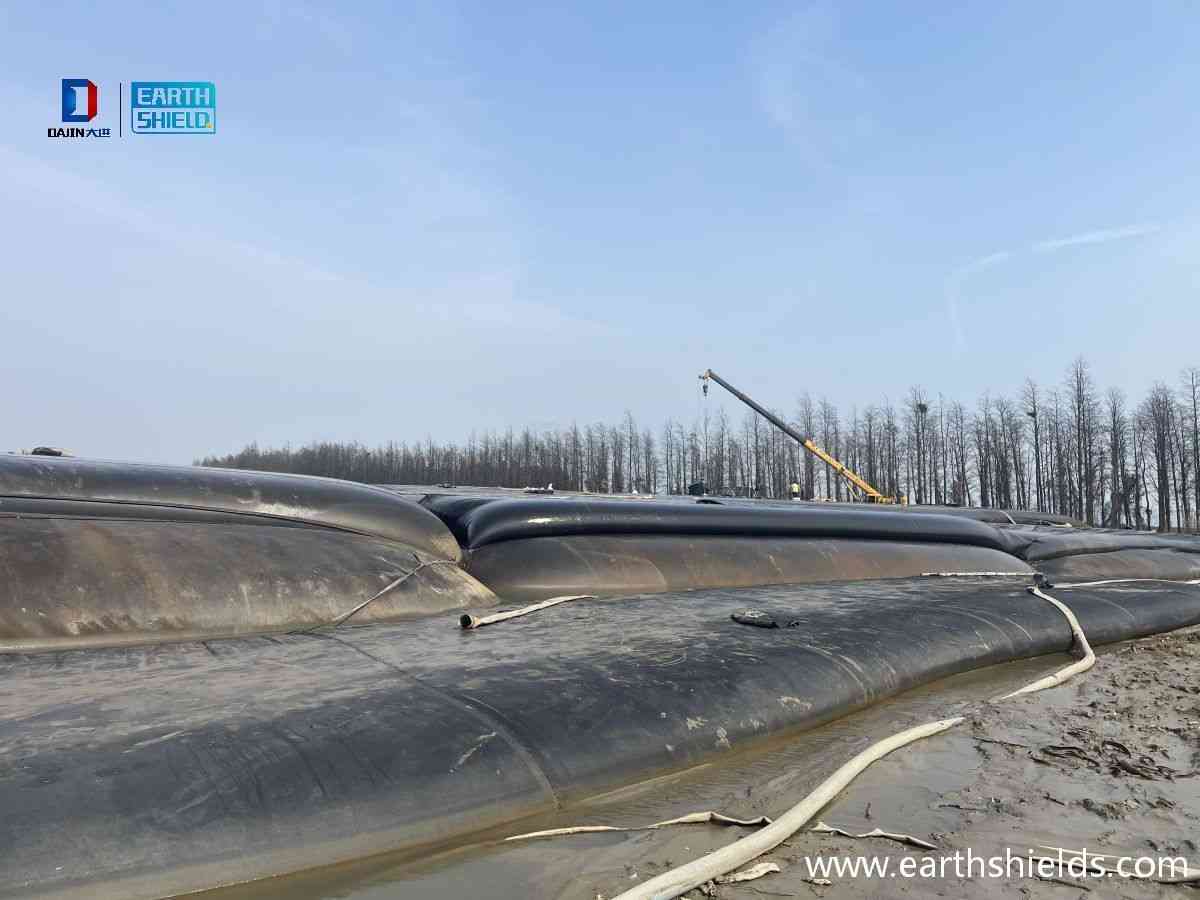
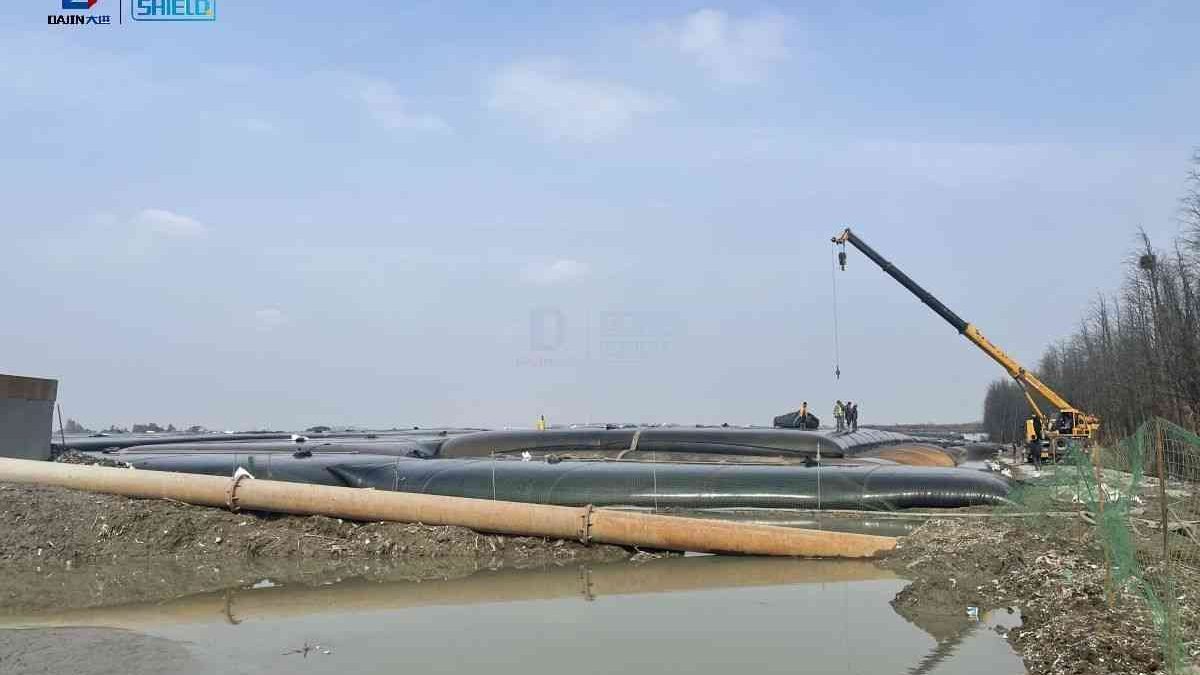
Moreover, geotubes are also applied in the process of sludge dewatering. The geotube dewatering technique offers an efficient way to separate water from sludge, which is beneficial in wastewater treatment and other industrial processes. This not only helps in the proper disposal of sludge but also in the recovery of water resources. Overall, the versatility of geotubes, whether for erosion control or sludge dewatering, makes them an indispensable tool in modern coastal and environmental engineering, contributing to the sustainable development and protection of our shorelines and water resources.


- High Strength and Durability: Generally made of high-strength geotextiles, they can endure significant pressure and tension. In harsh marine environments, under the impact of water currents and the weight of fill materials, they maintain structural integrity and have a long service life.
- Good Flexibility: They can be bent, folded, and shaped according to different terrains and engineering requirements, adapting to complex coastline shapes and irregular construction sites. This facilitates installation and layout. Moreover, when subjected to water flow and wave action, they can buffer energy through deformation, reducing the damage caused by impact forces to the structure.
- Filtration and Drainage Functions: The material of geotubes has a certain porosity, allowing water to permeate to a certain extent while preventing solid substances such as soil particles from being washed away with water, thus fulfilling both filtration and drainage functions. This helps maintain the stability of the fill material, preventing liquefaction or loss of the fill inside the tube due to water accumulation, ensuring the long-term effectiveness of the geotube structure.
- Construction Convenience: They are relatively light and easy to transport and handle. At the construction site, they can be quickly unfolded and filled, without the need for large professional construction equipment and complex construction techniques. This can significantly shorten the construction period and reduce construction costs, especially suitable for some urgent coastal protection or land remediation projects.
- Environmental Friendliness: Mostly made of environmentally friendly geosynthetic materials, they have a relatively small impact on the surrounding soil and water environment. After the end of their service life, the materials can be recycled or undergo relatively simple disposal, meeting the requirements of modern environmental protection projects and reducing the long-term burden on the environment.
- Cost-Effectiveness Advantage: The cost of raw materials is relatively low. Combined with its features of simple construction and short construction period, geotubes offer high cost-performance in many engineering projects. They can effectively control the overall project investment while ensuring project quality, providing an economical solution for project owners.
- Strong Adaptability Advantage: Regardless of the complex terrain and environmental conditions, such as coasts with different slopes, areas with variable water currents, or the special terrains in mining sites, Geotube can be effectively applied through its flexible design and material properties. From coastal protection projects to various resource extraction scenarios, it can be custom-installed according to the actual situation, perfectly matching the needs of various project requirements.
- Economic Cost Advantage: In many projects, its raw material cost is relatively low, and it is easy to transport and install, reducing the input of a large amount of manpower, material resources, and heavy equipment. Especially in the construction of large-scale coastal protection facilities (such as Revetments, Breakwaters, etc.) and mining operations, it can significantly reduce the overall project cost and improve the efficiency of capital use.
- Environmental Protection and Sustainability Advantage: Made of environmentally friendly geotextile materials, it has minimal impact on the environment during production and use. Moreover, after the end of its service life, the material can be recycled or easily disposed of. In ecologically sensitive projects such as wetlands creation and island creation, it helps protect the ecological balance and reduces the damage to natural resources, conforming to the concept of sustainable development.
- Stable Structure Advantage: When constructing structures such as Dykes, Levees, and Sand dune cores, it can provide stable support and reinforcement, effectively resisting the erosion of external forces such as water currents and wind waves, maintaining the integrity and durability of the structure, ensuring the long-term stable operation of the project, and reducing maintenance costs and risks.
- Multi-functional Application Advantage: It is not limited to a single field but is widely used in multiple projects with different purposes, such as Revetments, Breakwaters, Dykes and Groynes, Levees, Sand dune cores, Wetlands creation, Island creation, Mining Operations, etc., demonstrating its diverse functional values. It provides a one-stop solution for engineering problems in different industries, reducing the dependence on a variety of different materials and technologies, and improving the convenience and integrity of project implementation.
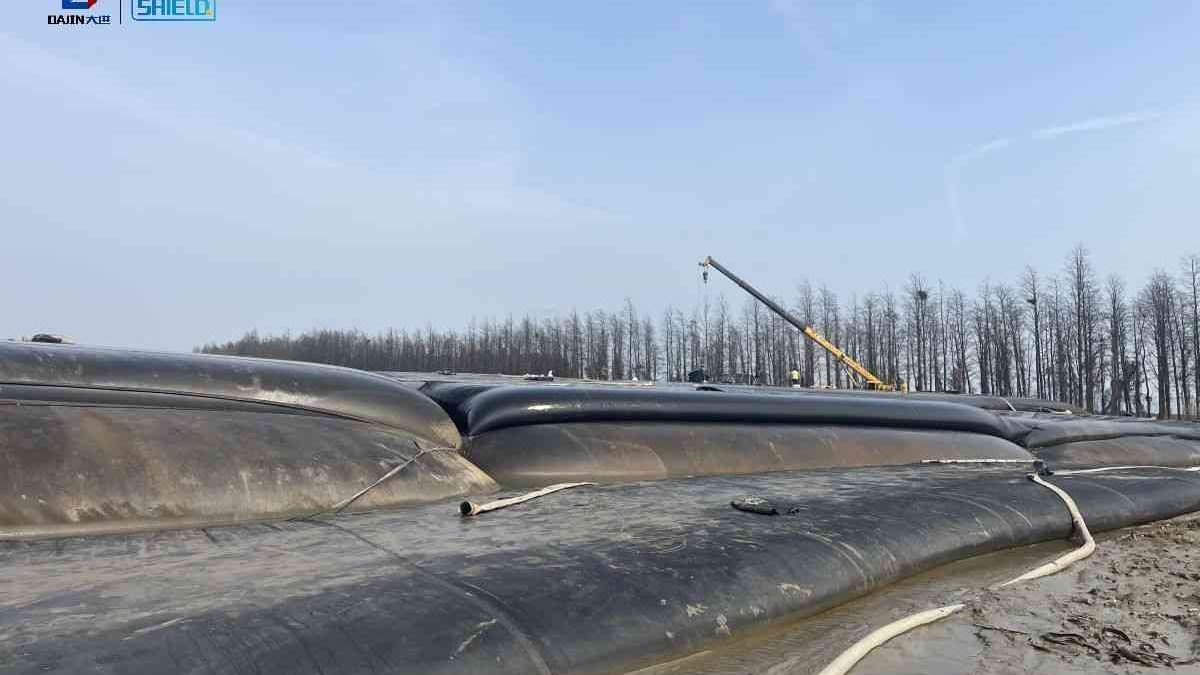
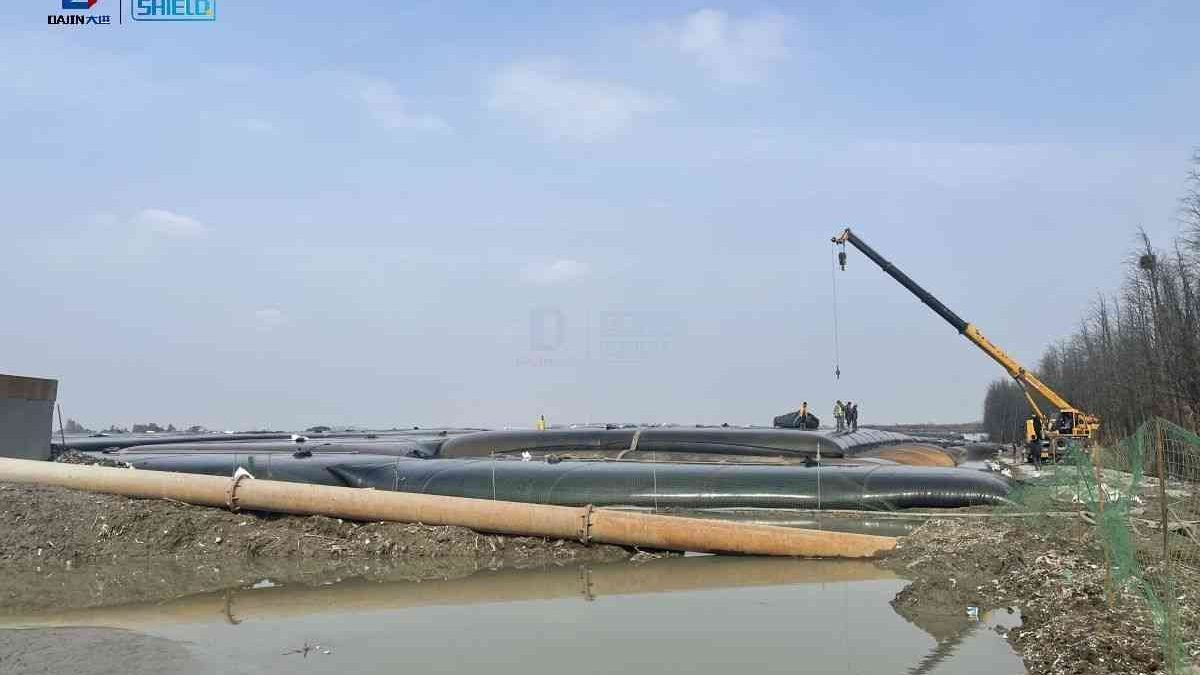


- Coastal protection and construction: Geotubes are used for breakwaters in hotels and seaside residences, slope protection in coastal and marine buildings, dams and groins, etc. to protect the coastline from erosion, such as providing a protective barrier for coastal properties, maintaining the stability of coastal structures, resisting the impact of waves, and ensuring the safety and stability of the coastal zone. It is easy to install and cost-effective. Geotubes of different specifications can meet diverse needs. They can also be used for seawall construction and enhance coastal protection capabilities. Relevant information can be obtained from channels such as Geotube youtube.
- Land reclamation and remediation: Geotubes can help land reclamation projects, such as building infrastructure in offshore areas, for land reclamation and forming new land, and can also be used to stabilize the core of sand dunes, prevent sand dunes from moving, promote the growth of sand dune vegetation, and maintain the stability of coastal dune ecosystems. At the same time, they are also used in wetland creation and island construction to provide support for ecological restoration and expansion of land area. Its price advantage makes it attractive in large-scale projects. Geotubes are also sold on the market.
- Industrial and environmental treatment: In mining operations, geotubes are used for tailings management, dewatering of wastewater treatment plants, sludge removal, and sedimentation dewatering. For example, they assist in copper removal in copper mining and are also used in agricultural composting. Geotube dewatering technology is used to achieve efficient solid-liquid separation and reduce environmental pollution caused by waste. The community exchange can share Geotube’s application experience and technology in various fields, help optimize installation and reduce costs. The cost of Geotube in different application scenarios varies depending on specifications and uses.
Technical Specifications: Details
- Material Properties: Made of high-strength geotextiles. Tensile strengths (in machine direction and cross-machine direction) vary according to applications, generally ranging from several kN/m to over 100 kN/m. Porosity is usually 10% – 50%. It has resistance to abrasion and UV degradation, with an expected lifespan ranging from several years to decades.
- Dimensions: Diameters commonly range from 0.5 meters to 3 meters or more. The length can be customized, ranging from several meters to hundreds of meters, depending on the project.
- Filling and Loading Capacity: The filling volume is measured in cubic meters, ranging from a few cubic meters to several hundred cubic meters, depending on the diameter, length, and design strength. The loading capacity is measured in terms of pressure (such as kPa) or the weight of the overlying material it can support, which is important for applications such as levees.
- Sealing and Connection Mechanisms: There are sealing methods such as heat-sealed ends or special mechanical fasteners. Connection methods include coupling devices, straps, overlapping and stitching, etc., ensuring the integrity of the overall structure when multiple geotubes are used.
- Permeability and Drainage Characteristics: The permeability is measured in cm/s or m/d. Some geotubes are designed with additional drainage features such as internal drainage layers or perforations, which are important for applications such as dewatering.
Geotube dewatering technology is a process that utilizes the unique properties of geotubes to separate solids from liquids, typically in the context of sludge or slurry. Here’s a step – by – step explanation of how it works:
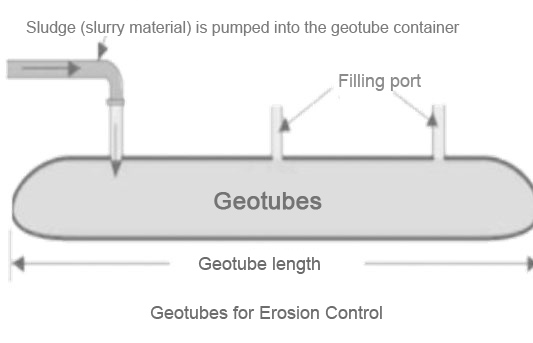
1. Filling the Geotube
The process begins with the filling of the geotube. The sludge or slurry, which is a mixture of solid particles and water, is pumped into the geotube. The geotube is usually made of a permeable geotextile material that allows water to pass through while retaining the solid particles.
2. Initial Filtration and Settlement
As the slurry enters the geotube, the larger solid particles start to settle at the bottom due to gravity. The geotextile material acts as a filter, preventing the solids from escaping while allowing the water to seep out. The porosity of the geotextile plays a crucial role here. It has a specific pore size that permits the passage of water molecules but restricts the movement of solid particles based on their size.
3. Pressure – Induced Dewatering
Once the geotube is filled, external pressure can be applied either through the weight of additional material placed on top of the geotube or through mechanical means such as squeezing or compressing the geotube. This pressure forces more water out of the slurry. The water migrates through the pores of the geotextile and drains away from the geotube.
The pressure also helps in compacting the solid content inside the geotube, reducing its volume and increasing the solids content percentage.
4. Osmosis and Diffusion
In addition to the physical pressure – driven process, osmosis and diffusion also occur. There is a difference in the concentration of solutes (dissolved substances) between the slurry inside the geotube and the surrounding environment. This difference in concentration drives the movement of water molecules through the geotextile in an attempt to equalize the concentration on both sides.
Diffusion of water molecules also takes place due to the concentration gradient. The water molecules move from an area of higher concentration (inside the geotube) to an area of lower concentration (outside the geotube).
5. Continued Dewatering and Stabilization
Over time, the dewatering process continues until an equilibrium is reached, where the rate of water seeping out slows down. The resulting dewatered material inside the geotube becomes more stable and easier to handle. It can then be disposed of or further processed depending on the requirements. For example, in sludge dewatering for wastewater treatment, the dewatered sludge can be more easily transported for final disposal or used for other purposes such as composting.
