Jing Ltd. products
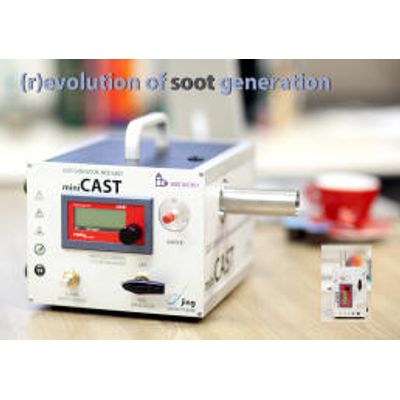
miniCAST - Model Series 6200 - Particle Monitoring Devices
miniCAST Series 6200 generate a small particle flow of 3 l/min (up to 30 mg soot /hour) with constant particle mass and number concentration. They allow testing particle monitoring devices for low particle flow and total mass output. The optional internal dilution air brings addtionally the particle concentration down to lower levels that allow measuring particle without any external diluting devices and saving expense respectively. The diluted particle flow can be directly let in to particle monitoring devices such as SMPS. The design and features of miniCAST Series 6200 meet the requirements of different applications in laboratories and for mobile needs.
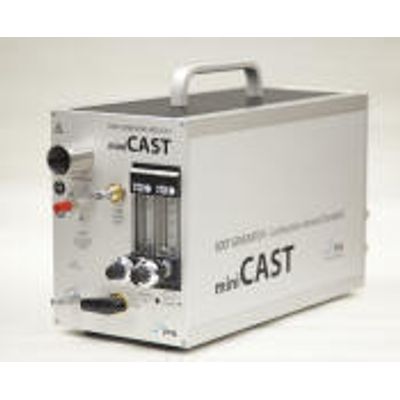
miniCAST - Model Series 5200 - Real Combustion Soot Particle
miniCAST Series 5200 produce real combustion soot particle by using a well defined flame that simulates the combustion in the modern combustion engines. The operation principle is based on solid know-how and practical experiences from more than 16 years leading aerosol research and development activities. miniCAST Series 5200 are designed for higher particle output. They supply up to 550 mg soot / hour with a flow rate of exhaust gases up to 30 l/min. Their design and features meet the requirements of different applications in industry and research laboratories and for mobile needs.
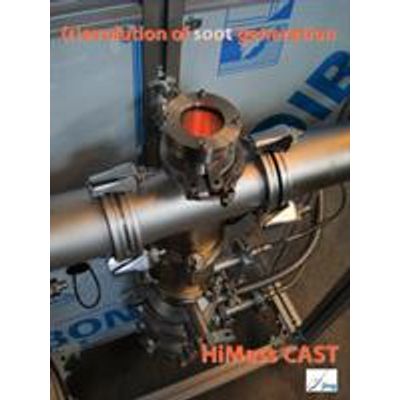
HiMass - Model CAST Series 7200 - Real Combustion Soot Particles
HiMass CAST has been constructed for applications with specific requirements on higher total flow rate and total soot mass output. Followings are some examples of the applications for HiMass CAST: Filter testing. Charging filter / loading DPF. Exhaust gas simulation. CVS calibration. Smoke simulation.
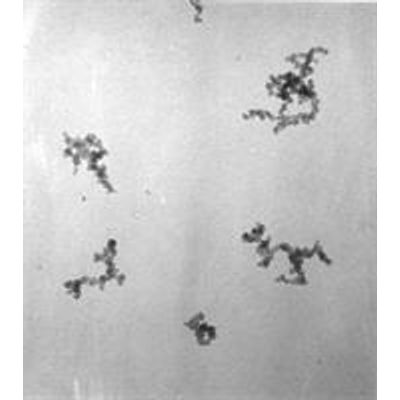
CAST - Model EC/OC - Soot Particles
Soot particles from CAST are agglomerate of spherical soot particles (primary particle) formed in the flame. The image of transmission electronic microscope (TEM) shows that their structure is the same as, e.g., the soot particles from diesel engine have
Flames
Diffusion Flame
In combustion, a diffusion flame is a flame in which the oxidizer, in our case the oxygen in the air combines with the fuel by diffusion. As a result, the flame speed is limited by the rate of diffusion. Diffusion flames tend to burn slower and to produce more soot than premixed flames because there is not sufficient oxidizer within the flame.
Premixed Flame
A premixed flame is a flame in which the oxidizer has been mixed with the fuel before it reaches the flame front. This creates a thin flame front as all of the reactants are readily available. If the mixture is rich, a diffusion flame will generally be found further downstream.