- Home
- Companies
- Ningxia Yongruida Carbon Co., Ltd.
- Products
- Yongruida - Cationic Polyacrylamide

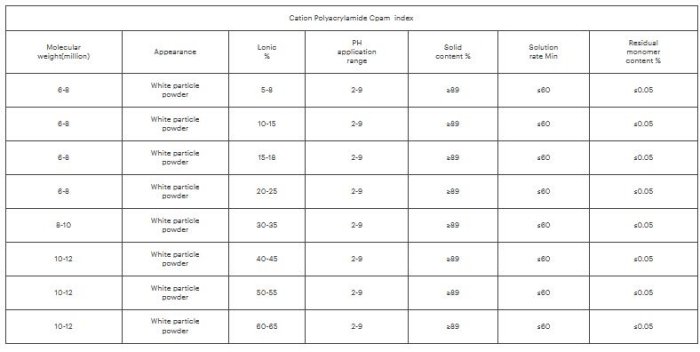
Yongruida - Cationic Polyacrylamide
Cationic polyacrylamide with high molecular weight could produce more stretching molecular chain in the water which will increase the capacity of adsorption and bridge for suspended particles flocculation. Moreover, the residual negative charge was balanced by cations between the chains which also served to hold the chains together. The mainly interaction mechanism between CPAM and suspended particles were static electricity, hydrogen bonding, covalent bond and van der Waals force. Base on these mechanism, the length of the chains mainly determined flocculation performance. Because of the differences in the length of the chains, the molecular weight of a polymer is determined on a statistical basis. Accordingly, how to obtain the higher molecular weight and higher solubility property of CPAM was the most critical point in the polymerization.
Cationic polyacrylamide copolymers (PAMs) are a group of water-soluble polymers with a wide range of applications in industry, food processing, agriculture and waste management. One of the major applications for Polyacrylamide is sludge dewatering in municipal waste water treatment plants. Spreading of the sludge on agricultural land is currently one of the most important recycling routes.
Synthesis methods of Cationic polyacrylamide :
The most important CPAM synthesis method was free radical copolymerization method, the basic reaction of polymerization usually expressed as Fig. In recent years, free radical polymerization method included four different synthesis technologies as follows:
- Aqueous solution polymerization
- Dispersion polymerization
- Inverse emulsion polymerization
- Photo initiated polymerization