


ESI - Model 9000A -XRF Stainless Steel Testing Instrument
Simply the Best Fast: Swiftly analyzes stainless steel in seconds to minutes. Multi-element: Detects various elements simultaneously. Non-destructive: Tests without sample damage. Accurate: Measures with high precision. Easy: Simple operation, user-friendly
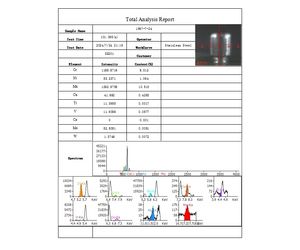
Stainless steel, a remarkable alloy, is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance and durability. Principally composed of iron, chromium, nickel, and other elements in varying proportions, it owes its unique properties to a carefully balanced chemical composition. The chromium content, typically exceeding 10.5%, plays a pivotal role. Upon exposure to the atmosphere, it forms a passive oxide layer on the surface. This nanoscale layer acts as a highly effective shield, protecting the underlying metal from rust and corrosion, even when subjected to harsh environments such as moist air, acidic media, or alkaline solutions. This alloy exhibits outstanding mechanical properties, characterized by a high strength - ductility combination. This enables it to be readily fabricated into an extensive array of shapes and products. Its applications span multiple sectors, from kitchen utensils and surgical instruments to building facades and industrial machinery. Stainless steel's inherent hygienic properties, stemming from its resistance to bacterial adhesion and growth, make it the material of choice for food processing and medical applications. With a diverse range of grades available, each tailored to specific performance requirements, stainless steel has found widespread use across industries as diverse as architecture, automotive, aerospace, and electronics. This ubiquity is attributed to its unique combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic versatility. The EDX9000A is a high - performance analytical instrument well - suited for accurately determining the elemental compositions of stainless steel. It can precisely quantify elements such as copper (Cu), chromium (Cr), arsenic (As), and silver (Ag), providing crucial data for quality control, material characterization, and research purposes within the realm of stainless steel production and application.

High Speed: Swiftly analyzes stainless steel samples
Accurate: Precisely measures elements like Cr, Ni, Mo and impurities, ensuring quality.
Non-destructive: XRF technique leaves samples intact, vital for costly or finished items.
Easy to Use: Simple operation, like handheld models with intuitive interfaces, needs little training.
Versatile: Tests various sample forms like solids, powders, liquids with minimal prep.

Metallurgical Industry: Used to analyze the composition of stainless steel, ensuring product quality and alloy consistency.
Mechanical Manufacturing: Essential for inspecting stainless steel parts and components to meet mechanical property and corrosion resistance requirements.
Aerospace Field: Helps to certify the high-quality stainless steel materials used in aircraft engines and structures.
Food and Medical Sectors: Verifies that stainless steel used in food processing equipment and medical instruments complies with safety and hygiene standards.
Waste Recycling: Determines the elemental content of stainless steel scraps for recycling and resource reutilization

Size of Spectrometer: 560mm*380mm*410mm
Size of sample chamber:460mm*310mm*95mm
Size of Vacuum sample chamber:Φ150mm×75mm
Weight: 45Kg
Element Range:Na11-U92
Analysis content range:1ppm- 99.99%
Detector:AmpTek high resolution SDD
DPP Analyzer: 4096 Channel DPP analyzer
Excitation Source:50W X-ray tube
HV unit:0-50kV
Power supply:220ACV 50/60HZ Environment:-10 °C 到35 °C
>Standard >Optional
Ag- Calibration standard Power stabilizer
Vacuum pump Alloy standard samples
Sample cup
USB cable
Power supply cable
Test Mylar
Calibration report
Warranty card

Stainless steel can be categorized through multiple approaches.
1. Classification by Chemical Composition
Chromium Stainless Steel: This type contains a chromium content typically ranging from 12% to 30%. For instance, Grade 430 stainless steel offers a cost - effective solution. Its corrosion - resistant properties make it suitable for applications like kitchenware manufacturing and building decoration projects, where it provides both functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Chromium - Nickel Stainless Steel: Grade 304 (18Cr - 8Ni) is a prime example of this category. Renowned for its outstanding mechanical and corrosion - resistant properties, it has found extensive use across diverse industries. From construction and automotive manufacturing to the production of household appliances, 304 stainless steel is highly favored due to its ability to withstand various environmental conditions.
Chromium - Manganese - Nitrogen Stainless Steel: This is a nickel - saving alternative. By substituting nickel with manganese and nitrogen, it not only reduces the cost associated with nickel usage but also retains many of the desirable properties of stainless steel, making it an attractive option in certain applications.
2. Classification Based on Metallographic Structure
Austenitic Stainless Steel: Grades 304 and 316 fall into this category. Characterized by their non - magnetic nature and high corrosion resistance, austenitic stainless steels are ideal for applications where exposure to corrosive environments is common. Their ability to maintain structural integrity in the presence of moisture, chemicals, and other corrosive agents makes them suitable for use in industries such as marine, chemical processing, and medical device manufacturing.
Ferritic Stainless Steel: Grade 430 is a representative ferritic stainless steel. It exhibits good resistance to chloride stress corrosion, which is particularly important in applications where the material may be exposed to chloride - containing environments, such as in some industrial settings or near coastal areas. As a result, it is used in specific fields where this property is crucial. Martensitic Stainless Steel: Grade 410 is a typical martensitic stainless steel. One of its key features is the ability to be strengthened through heat treatment processes. This makes it suitable for applications that demand higher strength, such as in the manufacturing of cutting tools, shafts, and other components where mechanical performance is a critical factor.
3. Classification According to Usage
Atmospheric Corrosion - Resistant Stainless Steel: Designed specifically for outdoor structures, this type of stainless steel can withstand the harsh effects of the atmosphere, including rain, humidity, and air pollutants. It ensures the long - term durability and structural integrity of outdoor buildings, bridges, and other architectural elements.
Acid - Resistant Stainless Steel: Intended for use in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries, this grade of stainless steel can resist the corrosive effects of various acids. It is crucial for equipment and pipelines in chemical plants, where the material must maintain its integrity in the presence of highly reactive chemical substances.
Alkali - Resistant Stainless Steel: Used in industries such as paper - making and dyeing, where the material is often exposed to alkaline substances. It can withstand the corrosive action of alkalis, ensuring the proper functioning of equipment and machinery in these industries.
Food - Grade Stainless Steel: This grade is strictly regulated to meet high safety and hygiene standards. It is used in food processing and catering applications, such as food processing equipment, kitchen utensils, and food storage containers. The material's resistance to corrosion and bacterial growth ensures that it does not contaminate food products, thus safeguarding public health.
