

- Home
- Companies
- Poly Processing Company
- Products
- Poly Processing - Ferrics, Alums and ...

Poly Processing - Ferrics, Alums and Polymers
Containing chemicals that react to their environment. Ferrics, alums and polymers are commonly used to treat water and wastewater. There are several reasons why these substances require specialized storage: Separation, settling and coagulation are major issues with these chemicals – and those conditions can be compounded by temperature variations. Settling and separation issues can lead to difficulty in pumping the chemicals. The chemicals are often delivered at elevated temperatures, testing the expansion and contraction capabilities of a tank. Ferrics create fumes that can defoliate surrounding trees and plants. Polymers can act as an environmental stress-cracking agent.
By providing the right kind of storage for these chemicals, safety can be maintained - and the integrity of the product can be preserved.
The Poly Processing System for Ferrics, Alums and Polymers
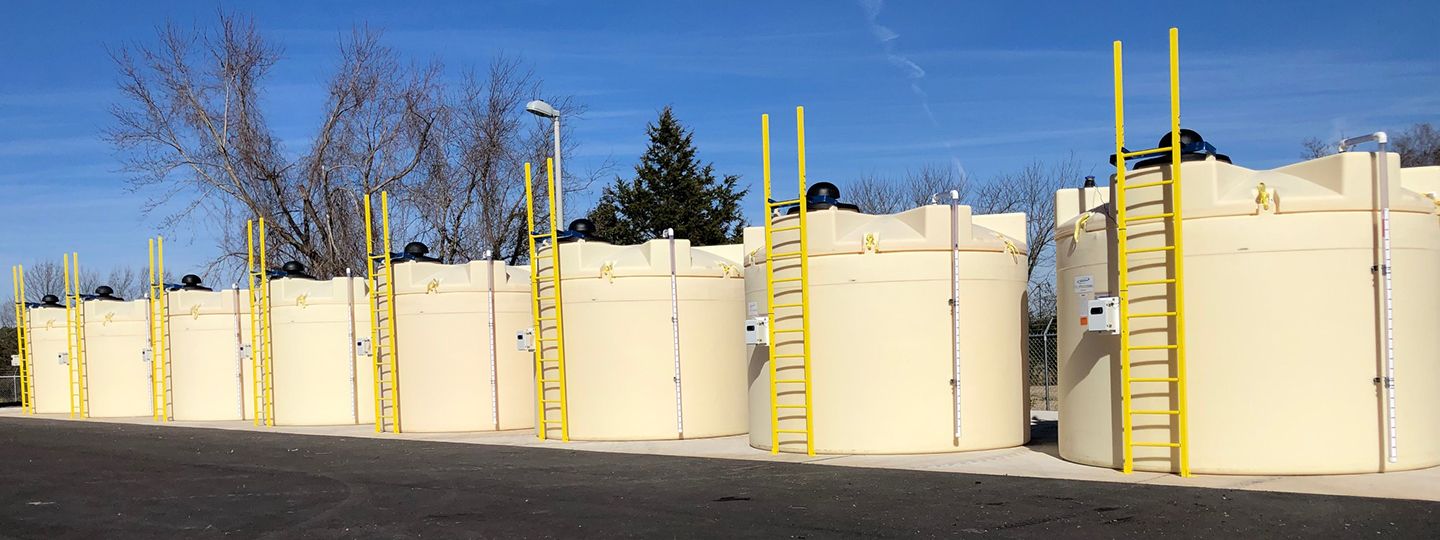
Several of Poly Processing’s features can make your storage system work for handling ferrics, alums and polymers. An IMFO® system is ideal for sludge control and ease of cleaning, since the tank drains at its true bottom. Heat pads and insulation can help keep the chemicals at the optimal temperature, greatly reducing the chance of separation and settling.
A mixing system can also be installed to keep the chemicals from separating – and a scrubber can help reduce the effects on foliage if you’re venting outdoors.
As for handling elevated temperatures – this is where the strength of the XLPE tank comes in. The crosslinked construction of these tanks allows for greater expansion and contraction, while maintaining structural integrity, lessening your risk for tank failure.
For additional information on storing ferrics, alums, and polymers, including recommended storage tanks and components, download our Ferrics, Alums & Polymers Guide below.
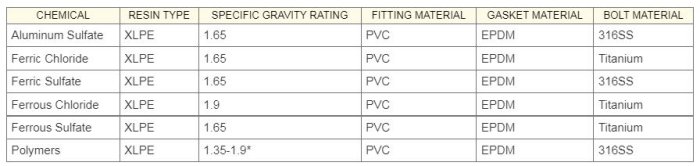
Tank options include:
- High-density crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE) construction for maximum strength
- OR-1000™ antioxidant inner surface
- Integrally Molded Flanged Outlet (IMFO®) for complete drainage
- SAFE-Tank® design for “tank-within-a-tank” protection
IMFO® Vertical Flat Bottom of XLPE:
- 230–13,650 gallons
- Appropriate spg rating for chemical as shown in Chemical Resistance Chart
Non-IMFO® alternatives:
Standard Vertical Flat Bottom XLPE:
- 30–13,650 gallons
- Appropriate spg rating for chemical as shown in Chemical Resistance Chart
SAFE-Tank® XLPE:
- 55–8,700 gallons
- Appropriate spg rating for chemical as shown in Chemical Resistance Chart
- Spg ratings for secondary tanks ≥ 3,000 gallons may be equal to or 1 less spg than primary tank.
- All other tank sizes must equal primary tank spg rating.
Alternative secondary containment: PPC secondary containment basin or other secondary containment suitable for ferrics, alums and polymers, of adequate size for use
Plumbing: Requires use of flexible connections with fittings on lower third of sidewall. See Fittings & Accessories for flexible connections options.
Expansion joints must meet the following minimum requirements:
- Axial Compression ≥ .67"
- Axial Extension ≥ 0.67"
- Lateral Deflection ≥ 0.51
- Angular Deflection ≥ 14°
- Torsional Rotation ≥ 4°
Venting: See Venting Chart
Foundation: PPC IMFO® tank pad or smooth concrete, asphalt or solid steel foundation designed to accommodate IMFO®, SAFE-Tank® or vertical tank
Temperature: Product should not exceed 100°F at delivery or during storage to maintain ASTM D1998 design parameters. Contact Customer Support if chemical is to exceed 100°F.
Lid: SAFE-Surge® manway cover for pneumatically loaded tanks; bolted manway cover for all other applications
Options: Restraint systems for wind and seismic, level gauges, ladders, heating pads, insulation, fume-tight manway cover, mixer mounts, OR-1000™ for NSF-61 certification and engineering stamp
