

- Home
- Companies
- Ball Corporation
- Products
- ATHENA - Model OAWL EVI-4 PROPOSAL - ...
ATHENA - Model OAWL EVI-4 PROPOSAL -International Space Station Orbit
3D winds are the horizontal vector component of the 3D wind field. 3D winds are one of greatest observation gaps in the operational weather community.
3D wind measurements would benefit:
- extreme weather forecasting
- civil aviation
- military operations
- air quality forecasting
- commerce
The first Optical Autocovariance type receiver was built at Ball starting in 2004 under Internal Research and Development (IRAD) funding. In 2008, under an Instrument Incubator Program grant from the NASA Earth Science Technology Office, Ball built the system into a full prototype of the Optical Autocovariance Wind Lidar (OAWL). Since then, Ball has partnered with NASA’s Earth Science Technology Office to further develop the mission concept and perform system validation.
ATHENA-OAWL Airborne Demonstrator
Ball has designed, built and validated multiple versions of the OAWL system. The most recent is a 532 nm Green-OAWL (GrOAWL). GrOAWL underwent airborne testing aboard the NASA WB-57 aircraft in summer 2016. Airborne testing serves to validate this future space-based system for ATHENA-OAWL.
Pictured:
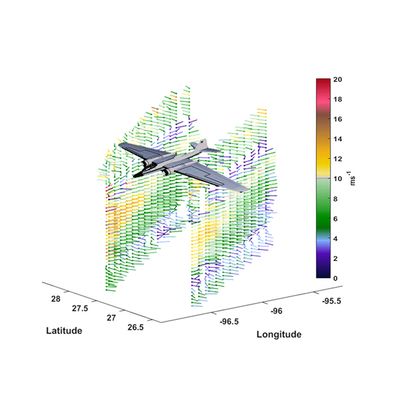
GrOAWL wind speed and direction profiles are derived using two-look line of sight OAWL Doppler measurements acquired over the Gulf of Mexico on 17 June 2016. The wind barb colors indicate the speed, and the barbs are pointing into the direction of the wind (i.e. winds around 4 km are mostly easterly, while winds above 6.5 km are more Northerly). The six slanted wind barb profiles shown in bold indicate speed and direction as measured by radiosondes dropped from the aircraft to validate the lidar measurement.
Ground and airborne based validation
Ball`s HAWC-OAWL (High spectral resolution lidar for Aerosols, Winds and Clouds) enables simultaneous Earth science measurements of winds and aerosols required for weather and air-quality forecasting. This instrument will advance the study of impacts of dust and aerosol transport on a global energy and water cycles, air quality and climate.
