

- Home
- Companies
- Premier Tech Water and Environment
- Products
- Premier-Tech - Moving Bed Biofilm ...

Premier-Tech - Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors (MBBR)
A moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) is the ideal wastewater treatment system for commercial, community, institutional, municipal, and industrial projects with continuous fluctuations in flow and strength. The Rewatec MBBR is suitable for flows of up to 20,000 m3 per day. Pre-engineered and ready to use, it manages domestic and high organic loads in all seasons, reducing soluble CBOD5 by up to 99% and NH4 by at least 94%.
The Rewatec MBBR offers many advantages over other wastewater treatment technologies:
- high efficiency reduces operating costs
- designs adapted to your unique needs
- components suited to your terrain
- more compact than traditional systems
- blends into your landscaping
The Rewatec MBBR system is most often a solution for:
- restaurants
- gas stations
- wineries and microbreweries
- hotels and inns
- campgrounds and parks
- food processing plants
- residential and municipal developments
- retrofits with existing infrastructure
How do our MBBR systems work? Primary treatment tank or fine screen
In typical installations, wastewater first flows into a primary treatment tank that allows liquids to separate from solids. Primary sludge that settles on the bottom of the tank is removed by a septic pumper as often as needed.
In some systems, a fine screen is used instead of a primary treatment tank. This simple barrier removes wastewater solids before they can move downstream.
Equalization tank (if needed)
After primary treatment, liquids move downstream and enter an equalization tank. This tank collects wastewater from daily peak-use periods and then sends controlled doses to the Rewatec MBBR.
Rewatec MBBR
Inside the Rewatec MBBR, microorganisms grow on floating biofilm carriers. They feed on organic wastewater pollutants, producing effluent composed of biomass particles and treated wastewater.
Our plastic biofilm carriers are specially shaped to increase the surface area on which microorganisms grow. This maximizes their ability to treat wastewater and helps you minimize the size of the reactor.
Bubbles continuously mix the contents of the Rewatec MBBR to ensure optimal contact between wastewater and microorganisms. Again, this improves their ability to remove wastewater pollutants.
Clarification tank and final discharge
After treatment in the Rewatec MBBR, wastewater flows into a clarification tank, where liquids are separated from biomass.
Sludge is sent back to the primary treatment tank or a sludge storage tank. Liquids are sent downstream for additional treatment or for safe discharge into the environment.
Local expertise is the cornerstone of our global team. Together, we have the technical understanding and industry experience to guide every phase of your project.
Design
- engineering support to guarantee the best solution
- help with technical drawings and diagrams
- advice for electromechanical equipment
- control panel design, including electrical diagrams
- dedicated project managers
- fast answers to all questions
- on-site support to ensure high-quality installations
- real-time troubleshooting
- commissioning by a qualified technician
- verification of installation success
- rapid responses to any areas of concern
- full support from our process and mechanical experts
- maintenance services from local technicians
- remote support available
- Landfill leachate site (LES and LET)
- Composting site
- Other industrial sites generating leachates

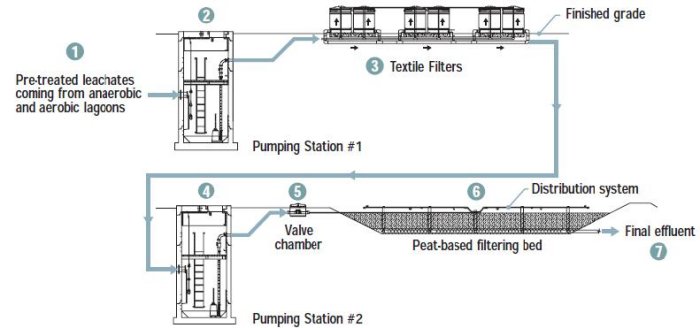
- Previously treated leachates by a series of anaerobic and aerobic lagoons.
- Factory-built pumping station including one or several pumps working alternately.
- The first polishing step consists of cells of Textile Filter units with composite filtering media allowing high pollutants oxidation.
- Factory-built pumping station including one or several pumps working alternately.
- Mechanical or manual valve chamber allowing isolation of each polishing field.
- The second polishing step consists of one or more peatbased filtering beds ensuring residual pollutants elimination.
- Effluent final disposal towards a watercourse or a ditch.
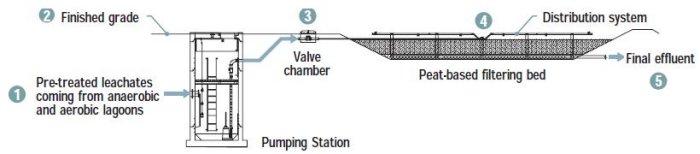
- Previously treated leachates by a series of anaerobic and aerobic lagoons.
- Factory-built pumping station including one or several pumps working alternately.
- Mechanical or manual valve chamber allowing isolation of each polishing bed.
- Polishing bed composed of a peat-based filtering media on which wastewater is distributed via a low pressure dosing system.
- Effluent final disposal towards a watercourse or a ditch.
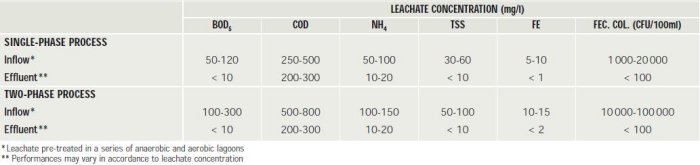

- Ammoniacal removal
- Passive disinfection (coliforms reduction)
- Modular construction, system can be easily expended as needs grow
- Controlled design flow of 5-200 m3/d (1,000 to 50,000 gpd)
- Low energy consumption
- Easy and economical maintenance and operation (no injection of chemical products)
