

Sequoia Scientific - Optical Volume Scattering Function (VSF) Sensors
The optical Volume Scattering Function(VSF) is an ‘inherent optical property’ of water that is used by optical oceanographers to predict light propagation, image degradation, remote sensed ocean color, biological environment etc. in water. Sequoia offers two instruments for this application. The LISST-200X and LISST-VSF. Respectively, these are for small-angle VSF and full-angle VSF with depolarization. Both measure beam attenuation. The VSF can be thought of as composed of forward scattered (0-90°) and back scattered (90-180°) light, typically denoted bf and bb, respectively. Back scattering, bb, is of interest for scientists and practitioners concerned with ocean color studies and remote sensing. Sequoia offers the Hyper-bb for measuring bb for these applications.
Small Angle VSF with the LISST-100X
The LISST-100X measures a weighted form of the VSF, covering the small forward range of angles, from 0.05 to 10° or 0.1 to 20°. No polarization information is available. The VSF measurements are offered at 32 log-spaced angles, i.e. successive angles increase by the factor 1.1809, beginning at the smallest values of 0.05 or 0.1 degree, depending on the model of instrument used, respectively C or B.
All measurements are made at the 670 nm wavelength of the laser. Measurements have been found to agree to few percent with Mie theory (see e.g. Agrawal (2005) in our library). Systems for the 532 nm green wavelength have been produced as custom units and remain available.
Small-Angle Depolarization with the LISST-STOKES
The LISST-STOKES from Sequoia is the world’s first commercially available submersible instrument for measuring depolarization in situ. This is accomplished using two independently switched, linearly polarized, fiber-coupled lasers. A 45° beam splitter divides the scattered light in two paths; one part scatters onto a ring detector from where the VSF is obtained. The other part of the light passes through an analyzer and is detected by a CCD array. From this measurement the depolarization ratio is obtained.
The instrument is designed for use in situ and can be submerged to a depth of 300m. Temperature and depth, as well as a measurement of the beam attenuation, is made for each measurement. Power is applied externally, either via an external power cable or an external battery pack (included).
The first LISST-STOKES shipped in August 2010.
Wide Angle VSF with Polarization, using the LISST-VSF
The LISST-VSF is an instrument that combines the small-angle VSF capability of the LISST-100X with a wide angle capability, and with additional information on polarization properties of the scattered light.
Like the LISST-100X, the LISST-VSF measures the VSF at small angles, 0.1 to 15-degrees with identical optics. Additionally, with a novel new ‘roving eyeball’ optics, it obtains a measure of the depolarization element P12, and a noisy estimate of P22.The roving eyeball covers the angles 15-160º.
The depolarization ratio is the ratio M22/M11, where M22 and M11 are Mueller Matrix elements. In the Mueller Matrix, M11 is the VSF. Any deviation of M22/M11 from unity is a measure of non-sphericity and can thus potentially be used for detecting bubbles and oil droplets.
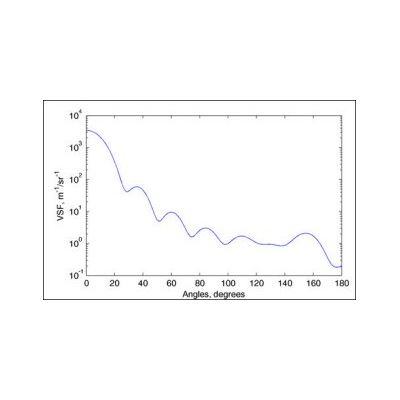
It describes the angular dependence of the fraction of incident light that scatters into different directions:
Integrating the VSF from 0 to 180º yields the total scattering coefficient, b [m-1].
Integrating the VSF from 0 to 90º yields the forward scattering coefficient, bf [m-1].
Integrating the VSF from 90 to 180º yields the backscattering coefficient, bb [m-1].
The VSF is identical to the P11 element of the scattering Mueller matrix of water.
Sequoia offers 3 instruments that measure the VSF: The LISST-100X, the LISST-STOKES, and the LISST-VSF.
