

- Home
- Companies
- Vista Clara, Inc
- Products
- Vista-Clara - Model GMR - Surface NMR ...

Vista-Clara - Model GMR -Surface NMR Instruments
Our flagship product, GMR™, is engineered for deepest possible groundwater imaging.
- Standard output of 600A and 4800V provides the highest power output of any surface NMR instrument, enabling resolution of aquifer properties to depths of up to 150 m (500 ft).
- Four full-capable Transmit/Receive channels with optional expansion up to 12 channels for efficient 2D profiling and noise cancellation.
- Non-invasive imaging of groundwater to depths of 150 meters
- Quantitative determination of water content
- Estimates of bound water volume and specific yield
- Relative or calibrated estimates of permeability
Non-invasively detect, measure, and image groundwater directly from the surface with Vista Clara’s GMR™ product family. Using a measurement loop of 2-150 m (6-500 ft) in diameter GMR™ uses the same NMR physics as MRI scanners. GMR™’s exclusive Multi-channel operation effectively cancels noice providing robust and accurate investigative outcomes.
Direct Imaging of Groundwater
GMR™ provides non-invasive detection and imaging of groundwater. This non-radiative measurement uses the Earth’s magnetic field to polarize the hydrogen nuclei of water. Alternating current pulses, routed through a wire loop on the surface, generate an alternating magnetic field in the subsurface, forcing the magnetic moments of the hydrogen nuclei to rotate in phase. This rotating magnetization from the groundwater is detected by the surface loop, as voltage signal, which is directly proportional to the volume of groundwater present in the formation. A forward mathematical model of the excitation profile is used to spatially invert and localize detected signals as a function of depth, yielding a 1D image of MR-detected water signals.
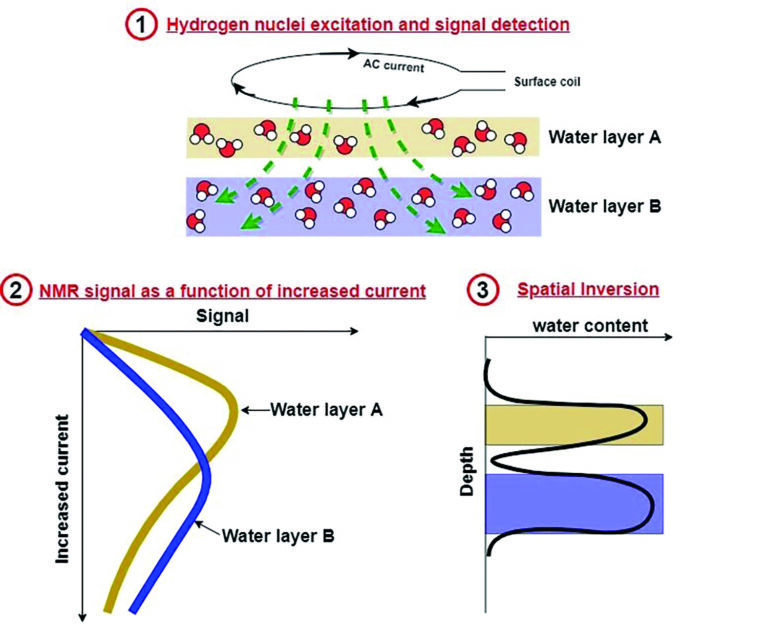
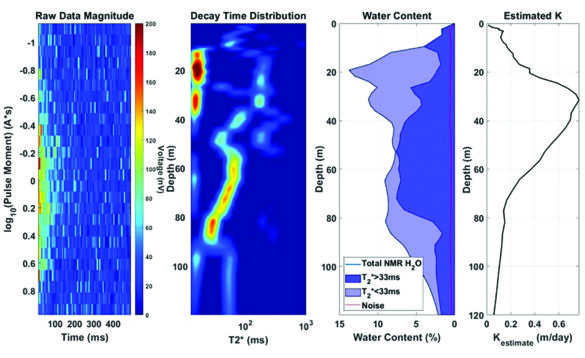
Time-domain analysis of the depth-localized NMR signals yields direct quantification of key aquifer properties, including:
- Volumetric water content, or porosity if the ground formation is fully saturated
- Differentiation of mobile water in large pores (specific yield) from bound water in smaller pores, through calculation of the NMR relaxation times (T1, T2, and T2*)
- Estimation of relative or calibrated hydraulic conductivity
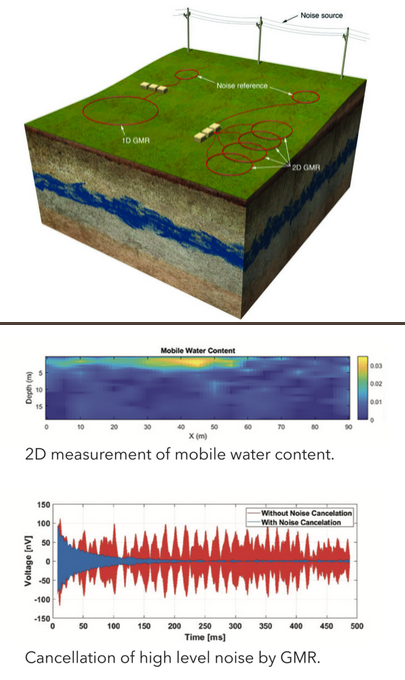
The unique multi–channel architecture of GMR™ adaptively cancels high levels of noise, improves data quality, and enables use close to powerlines and other infrastructure. Multiple independent Tx/Rx channels enable efficient 2D profiling. Simultaneous wideband response and high-speed sampling on multiple channels ensures robust measurement in all applications.
All GMR™ products incorporate advanced features that are essential to the performance, safety, and the user experience. All GMR™s have short dead times to capture short NMR signals of water in magnetic geology, in fine grained sediments, or in the vadose zone. Safety features are extensively integrated in the GMR™ design, protecting the user from powerful electric discharge
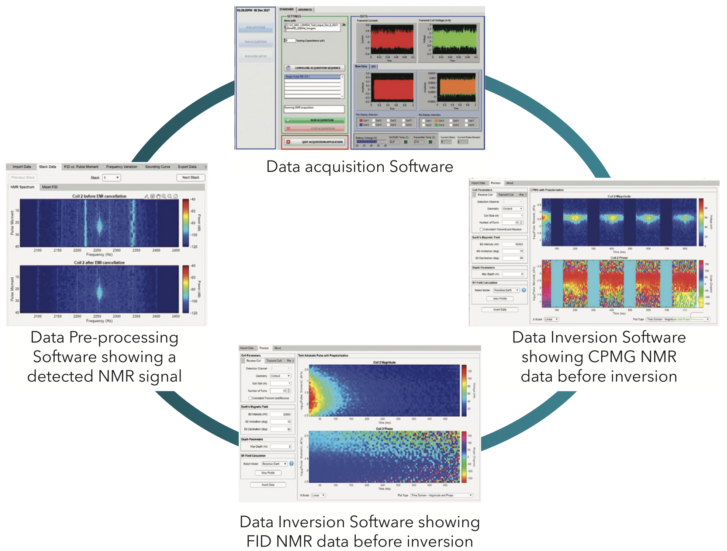
With GMR™’s full featured data acquisition and analysis software you can plan surveys, perform forward models and then see everything you need for your groundwater investigation while collecting data in the field. Additionally provided are:
- Advanced, proprietary pulse sequencest: adiabatic pulse for 2x-3x larger signals; CPMG for unambiguous detection of large pore water; and phase-cycling to prevent data artifacts.
- Monitoring of data quality and data processing in real time.
- Inversions in 1D and 2D using both resistive and conductive earth models.
- Estimates of bound/mobile water content and relative hydraulic conductivity.
GMR™ measurements can locate and characterize groundwater resources directly and non-invasively.
- Locate drill sites for groundwater production
- Delineate and characterize aquifer units for groundwater resource modeling and management
- Monitor changes in water table and saturation

