

- Home
- Companies
- Cambridge Environmental Research ...
- Software
- ADMS-Urban - Air Pollution Modelling ...

ADMS-Urban - Air Pollution Modelling Software
ADMS-Urban is a comprehensive system for modelling air quality in large urban areas, cities and towns. It is the only practical urban air quality model which incorporates the latest scientific understanding, explicitly represents the full range of source types occurring in an urban area, takes account of complex urban morphology including street canyons, and provides output from street-scale to urban-scale and, with the regional model link, to even larger scales.
- assessment of modelled air quality against air quality standards and limit values including those from WHO, EU, UK, USA and China
- developing and testing policy and action plans for air quality improvement at scales from street level (hotspots) to urban
- investigation of air quality management options for the full range of source types including transport sources
- source apportionment studies
- air pollution exposure studies
- air quality and health impact assessments of proposed developments
- provision of detailed street-level air quality forecasts
ADMS-Urban is being used across the world for air quality management and assessment studies of complex situations in urban areas, cities, towns and close to motorways, roads and large industrial areas.
Users of ADMS-Urban include:
- Over 80 local authorities in the UK for their Review and Assessment of air quality under the Local Air Quality Management program and for developing air pollution action plans and remedial strategies.
- London, UK: air quality management studies for the UK Department of the Environment (Defra); emission compilation and modelling assessment of proposals for Heathrow Airport for the Department for Transport; airTEXT air quality forecasting system
- China: Beijing: planning the large-scale development for the 2008 Olympics, air quality forecasting; Shanghai: city planning, traffic sources; Hong Kong: city planning, traffic and airport sources; 5 cities in Liaoning Province: industrial, heating (coal burning) and area sources.
- Budapest, Hungary: decision-making and air quality forecasting, large industrial sources and traffic sources.
- Johannesburg, Cape Town, South Africa: air quality management
- Environmental Protection Agency of Lithuania: air quality maps of urban areas
- Strasbourg, France: air quality assessment and forecasting.
- Rome, Italy: real time traffic management or “now-casting”, traffic sources.
- Bologna, Italy: assessment of new tram system, traffic sources.
- California, USA: health impact assessment.
- Singapore: air quality management studies for National Environmental Agency
- Barcelona: air quality forecasting
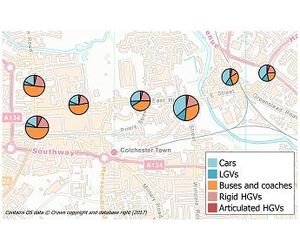
ADMS-Urban is distinctive in its ability to describe in detail what happens on a range of scales, from the street scale to the city-wide scale, taking into account the whole range of relevant emission sources: traffic, industrial, commercial, domestic and other less well-defined sources.
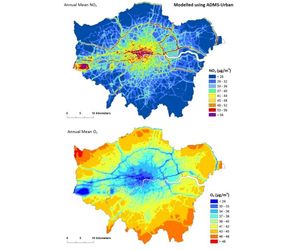
The science of ADMS-Urban is significantly more advanced than that of most other air dispersion models in that it incorporates the latest understanding of the boundary layer structure, using advanced algorithms for the height-dependence of wind speed, turbulence and stability to produce improved predictions. The model also takes account of the impacts of street canyons on dispersion, turbulence and mixing induced by traffic and includes a photochemical model for NOx and ozone.
This diagram shows some possible inputs to and outputs from the model, and some of the modelling options available.
Predicting pollutant concentrations from an urban area is a complex modelling problem. ADMS-Urban has been developed with a number of features to simplify the modelling process and help users. For example:
- Visualisation : ADMS-Urban has links to ArcGIS and MapInfo Professional GIS (Geographical Information System) packages as well as Surfer contour plotting package. The GIS link can be used to enter and display input data and display output, usually as colour contour plots.
- Emissions inventory : Source and emissions data can be imported from a Microsoft Access database created by the user or exported from CERC`s Emissions Inventory Toolkit, EMIT. EMIT contains current and future emission factors including those for vehicles, industrial processes and fuel consumption.
- Emission factors : Defra`s Emission Factor Toolkit emission factors.
- Intelligent gridding : ADMS-Urban includes an intelligent gridding option which places extra output points in and adjacent to road sources to give excellent spatial resolution in areas of particular interest.
- User-defined outputs : The user defines the pollutant, the averaging time (which may be an annual average or a shorter period), any percentiles and exceedence values that are of interest, and whether or not a rolling average is required. The output options are designed to be flexible to cater for the variety of air quality limits which can vary from country to country and over time.
In most cases, ADMS-Urban is first used to model the emissions from a base case scenario, that is, data (emissions, meteorology, background, etc.) are used to produce results that can be verified against locally monitored data from a recent previous year or the current year. Once the base case scenario has been validated, it is possible to investigate different scenarios, for example:
Impact of Major Development
ADMS-Urban is often used to compare air quality before and after major developments. An emissions inventory is compiled using the best available estimates for after the development. ADMS-Urban allows many What if? scenarios to be tried out, predicting concentrations at key receptors or across a wider area.
Future Years
The majority of air quality limits are objectives for future years. These scenarios can be modelled in ADMS-Urban using Defra`s Emission factor toolkit emission factors for future years, future predictions from EMIT or the user`s own estimate. Likely changes in traffic flows, fleet compositions and background concentrations if known, can also be included in the future scenarios.
Traffic Management
If the predictions for future years indicate that concentrations of certain pollutants are likely to exceed the objectives, it is usual to consider traffic management and emission reduction scenarios. For example, some local authorities in the UK are considering introducing Low Emission Zones within which only vehicles that have achieved a particular low-emission standard are allowed. The effect on air quality of introducing such measures can be investigated using ADMS-Urban. CERC`s Emissions Inventory Toolkit, EMIT can be used for investigating the effect on emissions.
One of the most important advanced modules in ADMS-Urban is the chemistry module. The following options are available:
- NOx – NO2 chemistry
- The Trajectory model
- Sulphate chemistry
Other advanced modules are:
- Street canyons
- Complex terrain
- Buildings
These modules are based on the latest understanding of the way these features affect the movement of airflow around the sources, and all have been shown to have considerable affect on observed concentrations.
Chemistry Module
In many urban areas, the dominant pollution source is road traffic, and the pollutants usually of major interest are NOx, O3, PM10 and PM2.5.
The ADMS-Urban models NOx chemistry using the 8 reaction Generic Reaction Set (Venkatram et al., 1994) that includes reactions with ozone and hydrocarbons.
The NOx chemical reactions take place over a relatively short time period and in order to get accurate predictions of NO2 concentrations, NOx chemistry should be taken into account. The Generic Reaction Set also predicts changes in ozone concentrations.
The Trajectory Model
A simple Lagrangian Trajectory Model is used to calculate background concentrations for the air approaching the main modelling area. This model includes the effects of emissions, chemistry, deposition and ozone entrainment.
By nesting the main model domain within a larger domain, such as a large urban conurbation, the Trajectory Model calculates a spatially varying background ambient concentration that takes into account the chemical reactions and processes occurring over the larger domain.
Sulphate Chemistry
The reactions between SO2 and other compounds in the air to produce particulates are based on those used in the EMEP model (Tsyro, 2001).
These reactions have a significant effect on the concentrations of particulates in areas where there are a large number of industrial sources emitting SO2 or downwind from a large emitter of SO2.
Street Canyons
`Street canyons` are defined as the deep, narrow, valley-like spaces created when a road is enclosed by tall buildings on both sides. High pollution levels are often observed in street canyons. The street canyon module included within ADMS-Urban/Roads is based on the Danish Operational Street Pollution Model (OSPM, Hertel and Berkowicz, 1990, Hertel et al., 1990).
Complex Terrain
This module is based on FLOWSTAR advanced airflow model which calculates the change in mean flow and turbulence due to terrain and changes in surface roughness (land use).
Buildings
Users can include the effect of up to 10 dominant buildings on point source emissions. ADMS-Urban creates an effective building for each point source from the user-defined buildings and models the re-circulating flow in the lee of the building, the cavity region, as well as the building main wake.
Emissions Sources
ADMS-Urban can be used to examine emissions from 7500 sources simultaneously, including:
- Road traffic, over 145,000 roads links (3000 road sources each with up to 50 vertices).
- Industrial sources, up to 1500 point, line, area or volume sources.
- Aggregated sources (grid source), up to 3000 grid cells can be used to model emissions from sources that are too small to define explicitly, for example, emissions from domestic housing.
Source parameters include:
- source location data,
- road widths and canyon heights for road sources,
- stack heights, diameters, exit velocities, etc., for industrial sources,
- grid dimensions for aggregated emissions data.
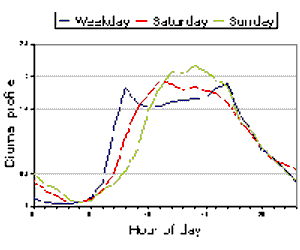
Emissions Profiles
- Up to 500 user-defined emissions profiles can be included in any modelling run to take into account the diurnal variation in traffic flows.
- Seasonal variations can also be included with up to 500 monthly profiles.
- Variation of sources with wind direction can also be modelled.
- For more detailed modelling, up to 500 annual hourly profiles can also be modelled.
Meteorological Data
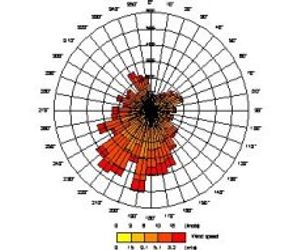
- A variety of meteorological data can be used for input and the format required is deliberately kept very simple.
- Wind speed, wind direction and temperature are required along with cloud cover, heat flux or solar radiation.
- The meteorological pre-processor calculates the necessary boundary layer parameters from the user`s input.
- There are a variety of suppliers of meteorological data across the world. A CERC meteorological data converter can convert METAR and otherNWSdata to ADMS format.
Traffic Flow
For road sources, the user can enter hourly speed and traffic flow data into the model and use ADMS-Urban`s built-in emission factors or, alternatively, the user can enter pre-calculated emissions data, for example emissions calculated within CERC`s Emissions Inventory Toolkit, EMIT, which includes many factors such as current and future factors for Euro standard engines. Modelling roads in urban areas is more complex than just modelling the emissions from traffic as a line source. Both the effect of street canyons and traffic-induced turbulence are included when roads are modelled in ADMS-Urban.
Background Ambient Concentrations
When modelling any local emissions, it is important to include the background ambient concentrations that are advected from outside the modelling area. Background ambient concentrations can be hourly values, or if these are not available, constant values can be assumed.
In the UK, these background data can be downloaded from the Defra website (http://uk-air.defra.gov.uk/data/) and included directly in any ADMS-Urban modelling scenario.
Aggregated Emissions
In urban areas, it is also important to include the aggregated emissions from sources that may be too small to define explicitly, but whose aggregate emissions contribute to overall pollution levels. For example, domestic emissions of NOx from an individual household may not be known, but the aggregated emissions could be calculated using area-wide figures for fuel consumption. In ADMS-Urban, a grid source with up to 3000 grid cells can be included in any run to represent these aggregated emissions.
Pollution concentrations can be calculated for averaging times ranging from seconds up to years. ADMS-Urban can calculate percentiles, the number of exceedences of threshold concentrations and rolling averages. These options allow users to compare concentration results directly with appropriate limits, for example those given by theUK NAQS,US NAAQS,EUorWHO.
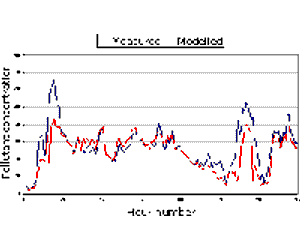
Model results are usually first verified by making comparisons with locally monitored data. This can be done by outputting results at receptor points corresponding to monitoring site locations. Modelled and monitored concentrations can then be compared as a time series plot.
Intelligent gridding
Results created by ADMS-Urban are often presented as colour contour plots. The intelligent gridding enables users to model a large area yet obtain high spatial resolution in areas of particular interest—in and around the roads. The ADMS-Urban contour plots are an extremely effective way of communicating results to decision makers, the public and other stakeholders.
Why do you need intelligent gridding?
Intelligent gridding gives high resolution of results where it is needed—in and around the roads. The three figures below show an area of 1.4 km2 with approximately 5-km length of roads being modelled.
- (1) shows concentration results using the intelligent gridding option, and
- (2) shows concentration results without the intelligent gridding option—this type of output is typical of other roads models that do not have the intelligent gridding option.

- The model interface is designed so that the user can enter the data required for the modelling in as straightforward a way as possible.
- The interface consists of several main screens. To set up a model run, the user simply works through the screens entering the relevant data or referencing external data files.
