

AnsTest - Aquifer Test Analysis and Interpretation
Pumping Tests
These are the most common aquifer test in which a well is pumped at a controlled rate and water-level response is measured in the same well or in surrounding observation wells. The tets are considered as the most reliable in determination of hydraulic properties.
Slug Tests
A type of field experiment where a slug of water is quickly (the interpretation assumes -instantaneously) added or removed from a groundwater well, and the water level response is monitored through time.
Stream-aquifer Tests
Combined analysis of well and stream hydrographs to determine properties of a stream bed and an underlying aquifer. This method can also be used to determine isolating properties of lake bottom sediments.
Pulse Tests
In a pulse test, an increment of pressure is applied to a well interval that is isolated by packers. zone. The decay of pressure is monitored within the same zone using automatic recording pressure transducers. This type of field experiments is most common in low-permeable rocks.
Constant-Head Tests
Aquifer test in which piezometric head (drawdown) in a well is maintained at a constant level while water discharge rate is monitored. A typical application is an aquifer test in a flowing artesian borehole with the potentiometric surface that is above the ground.
Analysis workflow: selection of analytical solution is easy with AnsTest-guided process.
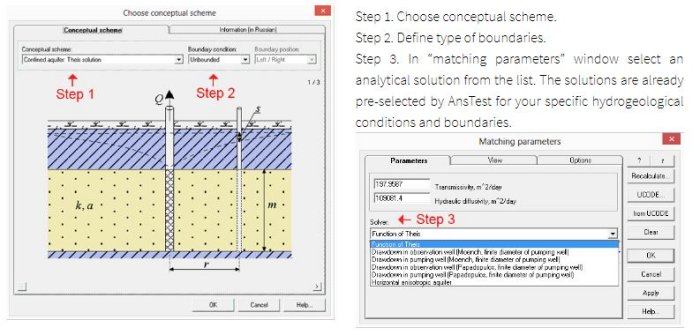
Supported type of hydrogeological conditions
- Non-leaky confined aquifer
- Point source in confined profile anisotropic aquifer
- Linear source in confined aquifer anisotropic on the vertical plane
- Unconfined aquifer
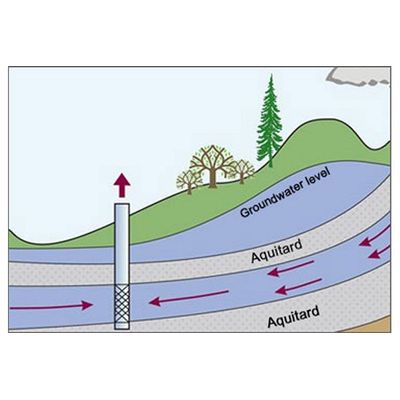
- Leaky aquifer system
- Two-layer aquifer system (unconfined aquitard above the confined aquifer)
- Arealy heterogeneous aquifer
- Pumping near river
- Multi-layer aquifer systems (two- or three-layer)
- Fracture
- Aquifer of infinite lateral extent
- Semi-infinite aquifers
- Strip aquifers
- Wedge-shaped aquifers
- Rectangular aquifers
- Circular aquifers
