

Arvato - Distributed Order Management Software
In the Distributed Order Management System all stocks, delivery points, articles, orders and customers are kept.
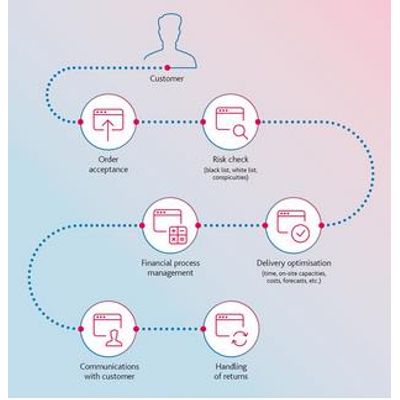
The prototypical process ("happy path")
The DOM accepts orders from various channels, such as the e-commerce system or the branch, and ensures optimal processing. The typical process flow, if everything goes according to plan, is as follows:
- Order is accepted
- Risk check (black list, white list, abnormalities)
- Determination of the optimal place(s) for delivery of the order based on various criteria such as time, stocks, capacities at the place of delivery, costs, forecasts, etc.
- Controlling the financial processes, such as triggering the capture of an order with credit card payment after the order has left logistics or calculating the amount to be paid in case of a return.
- Triggering of various communication processes and information, in particular to end customers, such as information to end customers that a product has arrived at a store and can be picked up
- Handling of the returns process
In order to be able to optimally calculate and control the delivery of end customer orders, basic data are required which are kept in the DOM. The most important "data pots" refer to the following areas:
- Articles: All articles relevant to the end customer are stored in the DOM, typically with basic information such as texts and images, regions, start-end, article combinations, accessories etc.
- Delivery locations: List of all locations from which articles are delivered, with master data and Omni-Channel relevant attributes such as geo-coordinates, opening hours or capacities
- Stocks: Current stocks of the relevant articles, including details of articles in transit and including non-physical articles such as services (e.g. bodywork services), gift cards or software rights
- Customers and orders: Since the system controls the processing of sales orders, it must also know all purchase orders and the corresponding customers. Customer orders usually refer to several articles and therefore to different order lines. Customer data can be transferred from the relevant e-shop system and all other ordering channels as well as from the stores (POS systems).
- Invoices, prices and promotions: In addition to the physical delivery process, the system also controls the respective financial process and accordingly creates data for a debtor management system, among other things. Accordingly, all prices, taxes, and promotions are stored in the system or can be retrieved from other systems.
Extensive functions for optimal control of the Omni-Channel delivery and financial processes. The DOM contains extensive business logic. One of the most important functions is Order Splitting & Routing - i.e. determining the optimal delivery location for an order. This is done on the basis of numerous parameters such as
