IFE Material Handling NA Inc. products
Screening Technology
Aeroselector
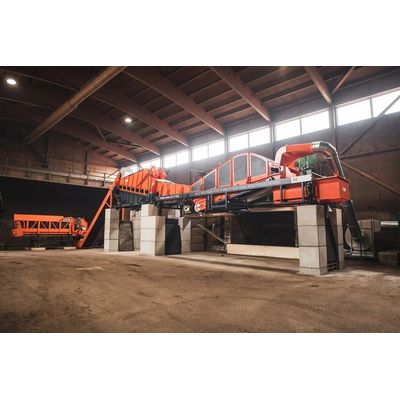
The new Aeroselector combines wind sifting, ballistic separation and screening in one machine. Its throughput but especially its compact design and its efficiency are very convincing. In professional composting plants this machine already proved itself successfully in separating foils, stones and structural material from the screen overflow. Also other moist and try material mixtures consisting of differently sized fractions can be split up effectively with this solution.
Magnetic Technology
Eddy Current Separator Inp Centric System
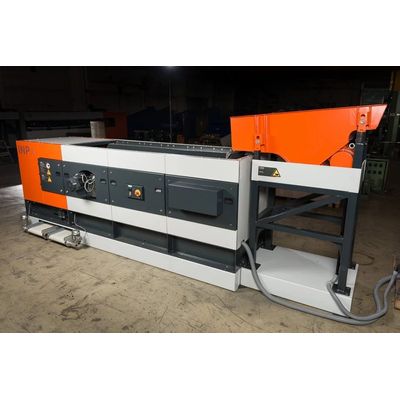
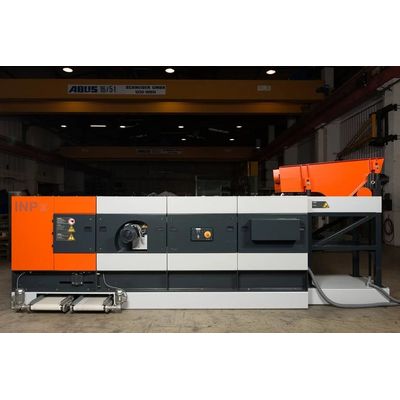
IFE eddy current separators are used to separate non-ferrous metals (aluminium, copper, brass, etc.) from bulk material of all kinds. The centric design IFE INP is used for the: removal of non-ferrous particles from bulk streams (biomass, waste wood, etc.). generation of non-ferrous concentrates (e.g. coarse material). separation of ubc (used beverage cans)
Eddy Current Separator Inp Eccentric
IFE eddy current separators are used to separate non-ferrous metals (aluminium, copper, brass, etc.) from bulk material of all kinds. The product portfolio of IFE comprises two special eccentric designs: The INPx VIOS is used for the: removal of non-ferrous particles from bulk streams (biomass, waste wood, etc.). generation of non-ferrous concentrates (e.g. WEEE, incineration slag, non-ferrous granules). separate conductors from each other (e.g. copper-lead granules, Zorba fractions). The INPx STRATOS is used for the: removal of non-ferrous particles from bulk streams (biomass, waste wood, etc.). generation of non-ferrous concentrates (e.g. WEEE, incineration slag)
Conveyor Technology
Scattering Plate
The inclined plate is arranged underneath a bin and is agitated to vibrate in longitudinal direction. This causes the material to flow. It is conveyed via a polished plate to the edge, where the materials falls in a curtain-like fashion. An even distribution is obtianed by minimizing the falling height between scattering plate and downstream surface.