- Home
- Companies
- ITASCA Software
- Software
ITASCA Software software
Consulting
Blo-Up - Hybrid Stress Blast Model (HSBM)
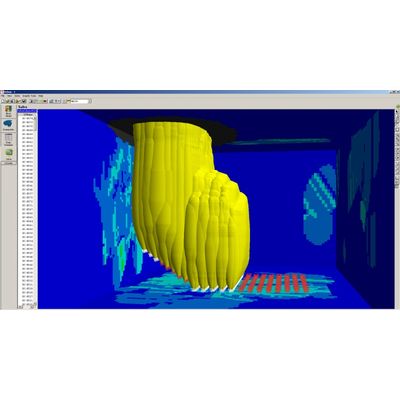
Since 2001, Itasca has been a member of the Hybrid Stress Blast Model (HSBM) project with the goal of developing a numerical model of the rock blasting process. The software created by Itasca, called Blo-Up, uses a unique combination of continuous and discontinuous numerical methods to represent the key processes occurring during blasting. Blo-Up is a three-component coupled model of rock blasting. A coupled modeling approach was chosen because no single numerical technique was found to adequately describe all the physical phenomena occurring during blasting. The three components are (i) a continuum geomechanics model for the early-time detonation and near-field crushing; (ii) a brittle discrete element model for stress wave propagation, fracturing and burden movement; and (iii) a gas product model for burden acceleration by gas expansion, fracture flow, and atmospheric venting.
Itasca - Model IHOD - Hydrologic Observation Dataviewer Software
IHOD (Itasca Hydrologic Observation Dataviewer) was developed by Itasca specifically for groundwater data management. IHOD is a customizable QGIS plugin that merges high-level database input/output with tools for viewing hydrogeologic and geochemical data. It interacts directly with underlying databases to retrieve data and provide the user with intuitive access to those data in graphical and tabular formats that are readily integrated into the user`s work flow.
Itasca - Model ReBop - Rapid Emulator Based on PFC Software
Itasca utilizes REBOP (Rapid Emulator Based On PFC) to simulate material drawdown within a block, panel, or sublevel cave mine by tracking the growth of draw zones (also called Isolated Movement Zones, IMZs) and corresponding fragmented rock flow associated with each drawpoint. The incremental laws governing IMZ growth and material movement in REBOP were derived on the basis of flow patterns observed in PFC3D and FLAC simulations of draw conducted by Lorig and Cundall (2000) and Pierce (2010) and in physical models conducted by a number of different researchers.
Itasca - Conventional Numerical Methods of Slope Analysis Software
Conventional numerical methods of slope analysis are mainly based on continuum approximation of the rock mass and the assumption of shear failure. Slope Model utilizes a novel approach that performs simulations of selected 3D sectors of rock slope stability in hard, fractured rock masses, consisting of any number of planar benches. The software implements a version of the Synthetic Rock Mass (SRM) approach (Pierce et al., 2007) applied to the specific case of rock slopes. SRM allows movement on joints (sliding and opening) as well as fracture of intact rock. The rock mass contains joint segments derived from a user-specified DFN (discrete fracture network).