

- Home
- Companies
- Altaca Energy
- Products
- CatLiq - Catalytic Liquefaction ...

CatLiq - Catalytic Liquefaction Nanotechnology
CatLiq (Catalytic Liquefaction) is a nanotechnology application used to convert organic waste and biomass to high quality bio-crude oil under supercritical conditions. The basic principle of this groundbreaking technology is to ensure formation of hydrocarbons, that is crude oil, by re-aligning Carbon (C) and Hydrogen (H) atoms with the help of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts developed by our company, after breaking off the bonds between the molecules in an alkaline environment, under very high temperature, and very high pressure. Water and minerals released during the process are separated and taken out of the system. This ensures continuity of manufacturing and the quality of the final product.
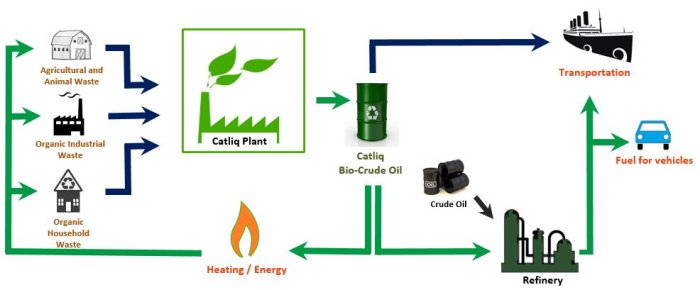
CatLiq is a "net energy" production technology that produces 7 units of energy for every 1 unit of energy used in the process. CatLiq produces 5 times more energy from 1 unit of organic waste in comparison to the biogas process. Furthermore, unlike gasification technologies, that only give good results with dry materials, CatLiq is specifically optimized for low-value wet waste such as sewage sludge.
The CatLiq Technology was invented by SCF Technologies, founded in 2003 by the 4 scientist owners who had been developing this and other critical technologies. SCF Technologies was listed in 2006 and its shares began to be traded on the Nasdaq OMX Nordic Exchange in 2007. Preliminary development work was completed in SCF laboratories, and was first tested in a purpose built pilot plant in Harlev near Copenhagen.
In 2006, a limited license agreement was signed by SCF with Grundfos Group for establishment of micro-scale facilities. A demonstration plant for micro-scale applications was designed and built for Grundfos by SCF Technologies’ engineers in 2008.

Altaca Energy, who had been following the development of CatLiq for a long time, took a strategic decision to acquire the IP rights covering all of CatLiq `s international patents and know-how, and also the pilot plant in Harlev, in 2011. Altaca Energy technical staff worked together with the Danish engineers on the dismantling of the pilot plant and the reinstalling / commissioning in the Gebze Organized Industry Technopark near Istanbul, in the same year.
Since acquiring the IP Rights, and installing the pilot plant in Gebze, Altaca Engineers have been working on further technological advances to both identify and eliminate weaknesses in the technology and, as a result, the efficiency of the process has been significantly improved. These improvements include the resolution of a problem with the decomposition of organic salts, the development of a new system for waste-water treatment and significant advances have been made to lighten the oil produced.
Catalysts are substances that increase the rate of a chemical reaction without themselves being consumed or changed in the reaction. The term catalyst was first used in 1835 by Swedish chemist Jöns Jakob Berzelius. Berzelius proved that the catalysts act so as to unbind the reactants and thus help the reaction to occur more rapidly.
Some catalysts slow down the reaction rate. These are called negative catalysts. However, most catalysts increase the reaction rate. Catalysts that increase the reaction rate are called positive catalysts. Catalytic processes are widely used in modern industry, mainly in chemical processes and in production of petroleum products.
Catalysts are divided into two groups:
- Heterogeneous catalysts are generally solid substances and the reactive components are generally in gas or liquid form.
- Homogeneous catalysts are in the same phase as the reaction components.
The basis for the huge potential of the CatLiq Process is the catalysts developed and owned by Altaca Energy. Thanks to these special catalysts, used in the correct amounts, the formation process of oil, normally taking place over hundreds of thousands of years by natural means, is replicated in the CatLiq reactors, with the whole reaction being completed in less than 30 minutes.
CatLiq technology is optimized to produce energy from wet waste and biomass containing more than 50% water, this contrasts with existing combustion and gasification technologies that can only work with dry waste and biomass.

CatLiq technology can process a wide range of raw materials, including no value or negative value organic wastes.
The main potential raw materials for the CatLiq process are:
- Treatment plant sludge
- Cattle waste
- Poultry waste
- Food industry residues
- Forest waste
- Residues of ethanol and bio-diesel production
- Algae
These raw materials can be used separately or mixed.
CatLiq process converts wet organic waste and biomass into four different product groups.
- Bio-Crude Oil
- Gas
- Minerals
- Waste Water
CatLiq Oil is a bio-crude oil with a calorific value of 35 MJ/I. This oil can be refined, without mixing, or can be mixed with fossil oils using existing facilities. The resulting products can be used as alternatives to fossil products.
The gas resulting from the process is used internally within the production process for heating. Water and minerals produced can be used as is, or they can be used to add value to other products in the advanced stages of the process.
