- Home
- Companies
- Global Advantech Resources Limited
- Products
- Global Advantech - Model TDS801 - ...

Global Advantech - Model TDS801 -Electrocoagulation and Advanced Electrochemical Oxidation
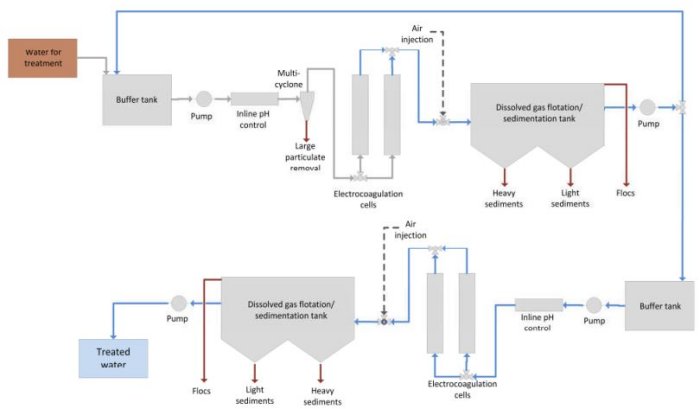
Electrocoagulation is an electrochemical process for the treatment of waste water, effluent, process water, produced water, bilge/ballast water, mine tailings, etc. The process was originally developed in 1906 to treat bilge water from ships, but was never adopted at the time due the lack of legislation concerning marine discharges.
Electrocoagulation is a proven and cost effective technology to treat and remove most contaminants/pollutants from water. It removes suspended solids, emulsified hydrocarbons and many dissolved organic compounds, heavy metals, (including chromium, cadmium, gold, platinum, radionuclides) and arsenic, bacteria, algae, larvae, etc., from water for re-use/discharge. The process may also be used to protect reverse osmosis elements, membrane filters, ion exchange columns, etc., from fouling. The process is continuous flow and is low in energy consumption.
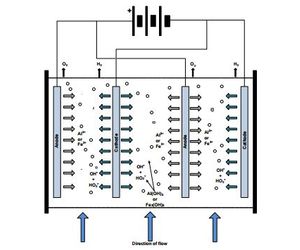
Electrocoagulation cells consist of pairs of parallel metal plate electrodes separated by a few millimetres with a low voltage applied at high current densities.
The current flowing between the electrodes destabilises electrical charges, which maintain suspensions of particulates, e.g. clays, and emulsions/micro-emulsions of hydrocarbons and insoluble organic compounds. The particulates coagulate together into flocs. The hydrocarbons and insoluble organic compounds coalesce into larger droplets and rise in the cells.
Electrochemical reactions at the electrodes produce very fine H2 and O2 gas bubbles and highly chemically reactive hydroxyl OH- and superoxide HO2 - radicals. The gas bubbles promote the flotation of coagulated solids and coalesced hydrocarbons, etc. The hydroxyl and superoxide radicals cause precipitation of hydroxides of heavy metals and breakdown of many soluble organic molecules.
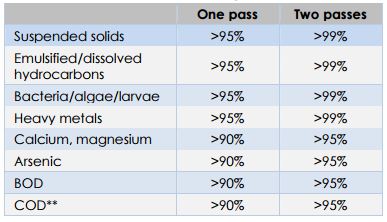
**Electrocoagulation cells remove compounds that cause BOD (biological oxygen demand) and COD (chemical oxygen demand) in wastewater and effluent. However, some soluble organic and ammoniacal compounds, sulphides and mercaptans may require additional treatment with advanced electrochemical oxidation for their removal. Volatile fatty acids (VFAs): acetic/ethanoic acid to valeric/petanoic acid (i.e. C2 to C5) cannot be removed by electrocoagulation or oxidation and must be removed with either membrane filtration or aerobic biological treatment. VFAs may occur in wastewater and effluent that has been stored in anoxic conditions and has undergone anaerobic fermentation, discharges from anaerobic digesters, drilling and production platforms (acetic acid is used for cleaning and well-stimulation), breweries and wineries, etc.
Global Advantech’s electrocoagulation systems contain a number of innovative design features and benefits to ensure effective and continuous operation:
Technology
- The cells use optimised low voltage, high current electrochemistry, with a large number of parallel plate electrodes for efficient operation.
- The cells have a hydrodynamic design, which ensures that flow is through the whole cell volume and electrodes are evenly consumed.
- The cells use upward flow to sweep out all hydrogen and oxygen bubbles produced during the process to flotation/sedimentation tanks and to prevent sediment build-up in the cells.
- All systems are PLC controlled, programmed to prevent metal plate passivation (development of an oxide layer, which acts as an insulator preventing cells from continuing to operate).
- Air is injected into the exit streams from the cells to enhance the flocculation and sedimentation processes.
- The cells discharge into integrated flotation/sedimentation tanks, with automatic floc scrapers and floc/sediment discharge pumps.
- Instrumentation options include plate wear monitoring and telemetry for remote monitoring.
Safety and ease of maintenance
- The electrodes are mounted in carrier cartridges enabling rapid replacement.
- Multi-cell configurations enable a single cell to be taken off-line for maintenance.
- All cells are mounted inside safety cages with interlocks to prevent access during operating.
Modular system design
- Electrocoagulation systems are available skidmounted or installed in container.
- Compact single and full-size multi-cell systems, capable of handling from 1m3 per hour to more than 200m3 per hour water flow available.
Operating environment
- Standard electrocoagulation systems are configured for safe area operation, systems may be configured to operate in ATEX 22 (Zone 2).
Other options available for Global Advantech’s electrocoagulation systems include
- Cavitation gas stripping system for pre-treatment of effluent steams to remove dissolved gases methane and ammonia, e.g. landfill leachate, produced water, etc.
- Advanced electrochemical oxidation cells to mineralise many soluble organic compounds to carbon dioxide water and simple salts, and oxidise sulphides and ammoniacal compounds (see later section).
- Final stage water treatment to remove chlorides, bromides, volatile fatty acids (acetic/ethanoic acid, etc.) from treated water to meet discharge criteria.
Treatment of contaminants/pollutants in solids
- Cavitation scrubbing systems plus specially formulated chemical agents may be used to extract/wash contaminants/pollutants from solids and solubilise them into water. The water is then treated using with electrocoagulation (see technology data sheet on cavitation scrubbing TDS805 and chemical decontamination product guides).