

AAT Bioquest, Inc.
- Home
- Companies
- AAT Bioquest, Inc.
- Products
- ER Tracer - Endoplasmic Reticulum ...
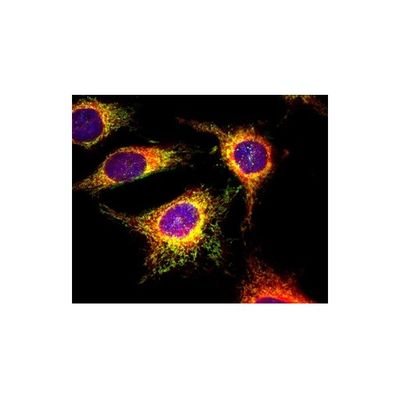
ER Tracer - Endoplasmic Reticulum Staining Kits for Live Cells
ER Tracer™ dyes are membrane-permeant stains considerably selective for the endoplasmic reticulum in living cells. As the key component in our Cell Navigator® Live Cell Endoplasmic Reticulum Staining Kits, ER Tracer™ dyes can be multiplexed with other fluorescent proteins or probes in live cell multiparametric studies or after fixation for colocalization studies. However, for certain cell lines, ER Tracer™ stains may not selectively bind to ER.
Most popular related searches
- Highly-selective for ER over other cellular compartments (e.g. lysosomes and mitochondria)
- ER staining well-retained after cell fixation
- Available in blue, green and red fluorescence to facilitate multiplexing with other fluorescent probes
- Suitable for proliferating and non-proliferating cells
- Kits includes a robust staining protocol and sufficient materials for 100 tests
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an organelle present in most eukaryotic cells. It is primarily responsible for the synthesis and transport of cellular products such as proteins, lipids and hormones. Structurally, the ER is comprised of an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs and tubules that extend from the nuclear membrane throughout the cytoplasm. These sac-like structure and tubules are held together and supported by the cytoskeleton.
The ER complex is comprised of two subunits - rough ER and smooth SER. The surface of the rough ER is coated with protein-manufacturing ribosomes. Once synthesized, membrane-bound transport vesicles shuttle these proteins to the Golgi apparatus. The smooth ER lacks ribosomes and is responsible for the synthesis of lipids, phospholipids and steroids. Secondary responsibilities of the smooth ER include carbohydrate and steroid metabolism, detoxification and modulation of calcium ions.
The ER complex is comprised of two subunits - rough ER and smooth SER. The surface of the rough ER is coated with protein-manufacturing ribosomes. Once synthesized, membrane-bound transport vesicles shuttle these proteins to the Golgi apparatus. The smooth ER lacks ribosomes and is responsible for the synthesis of lipids, phospholipids and steroids. Secondary responsibilities of the smooth ER include carbohydrate and steroid metabolism, detoxification and modulation of calcium ions.
