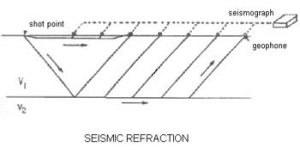
Seismic Refraction Technique
The refraction method uses seismic waves, introduced into the ground by a weight-drop source, to determine the compressional velocity of earth material. The seismic wave changes direction and speed, or refracted, as it propagates through the earth. When the refracted seismic wave impinges on an interface at a critical incident angle, the energy travels along the interface and sends seismic wavelets back to the surface. Geophones placed at selected intervals along the ground surface detect the ground motion and send an electrical signal, via a cable, to the seismograph. The seismograph digitizes, amplifies, filters and records the incoming signals. Analysis of the arrival times of the refracted wave provides a means for calculating the seismic velocity and modeling depths to subsurface layers.