

- Home
- Companies
- Sepax Technologies, Inc.
- Products
- Sepax Proteomix - Columns

Sepax Proteomix - Columns
Proteomix ion-exchange phases have been innovatively developed for achieving high ion-exchange capacity, a breakthrough technology for non-porous resins. Proteomix packing support is composed of a rigid, spherical, highly cross-linked poly(styrene divinylbenzene) (PS/DVB) non-porous bead with particle size selections of 1.7, 3, 5 and 10 µm. The PS/DVB resin surface is grafted with a highly hydrophilic, neutral polymer thin layer with the thickness in the range of nanometer. The hydrophobic PS/DVB resin surface is totally covered by a hydrophilic coating that eliminates non-specific bindings with biological analytes, leading to high efficiency and high recovery separations for biological molecules. On the top of the hydrophilic layer, ion-exchange functional groups are attached via a proprietary chemistry, resulting in a high capacity ion-exchange layer.
Non-porous Proteomix ion-exchange phases are unique because they combine increased capacity and resolution with their intrinsic advantages of high efficiency and high separation speed. Proteomix ion-exchange phases are especially suitable for high resolution, high efficiency and high recovery separations of proteins, oligonucleotides, peptides, polysaccharides, cell lysates, nanoparticles and nanotubes.
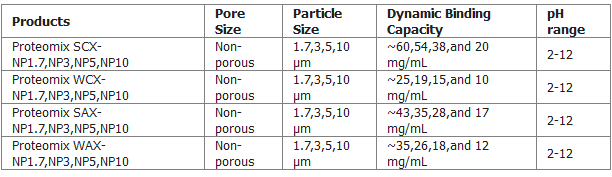
As shown in Figure above, Proteomix SCX, WCX, SAX, and WAX are strong cation exchanger with sulfonate functional groups, weak cation exchanger with carboxylate functional groups, strong anion exchanger with quaternary ammonium functional groups, and weak anion exchanger with tertiary amine functional groups, respectively. All ion-exchange groups are chemically bonded to the hydrophilic layer coated on non-porous PS/DVB beads.
- Uniform polymer beads as the packing support
- Proprietary surface chemistry specially designed for elimination of non-specific bindings
- Tunable separation capacity with combination of the pore structure and the controllable surface chemistry
- Unprecedented separation efficiency, selectivity and resolving power
- Complete selection for analytical, semi-preparative and preparative separations
- Wide particle size selection
- High stability
- High recovery
- High lot-to-lot reproducibility
- Well suited for UPLC system
Figure below is a typical test chromatogram for a Proteomix SCX-NP column (3 µm). Extremely high efficiency separation was achieved for 5 proteins. Those proteins were eluted based on their charge state (pI) from low to high: ovalbumin, ribonuclease A, cytochrome C, aprotinin, and lysozyme. At the separation conditions (pH 6.0), ovalbumin is negatively charged and eluted at the void volume, indicating no non-specific bindings.
