

- Home
- Companies
- Shanghai VOR Separation Technology ...
- Products
- VOR - Belt Filter Press
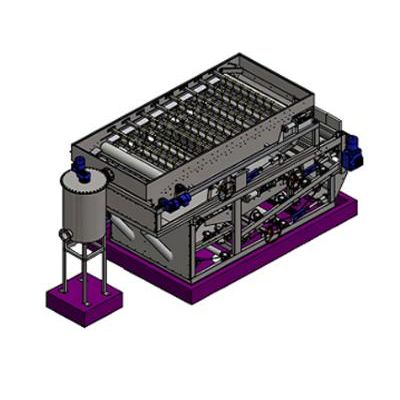
VOR - Belt Filter Press
Belt Filter Presses use filter belts (typically polyester) are intended for mechanical dewatering of waste water sludge and also of the water conditioning sludge and of the industrial slurries. Belt filter presses are used overall at the waste water treatment plants due to its high productivity and reliability.
Belt Filter Press originated in Finland is designed with long term value and includes many innovative features that provide high performance in a compact, high value package. Many competing products are based on old and inferior designs that do not utilize filtration area effectively. Stainless Steel frame and roller construction are standard. The optional touch screen and PLC integrate the press and support equipment so that unattended operation and integration into central control systems are easily accomplished.
Typically, dewatered sludge of wastewater treatment plants after belt filter press reaches about 18-35% cake solids under receives a slurry ranging from 0.8- 4% feed solids, and at average polymer dose 2-3.5 kg/t of the sludge dry matter(DS). Performance depends on the nature of the biosohds being processed.
How Belt Filter Press Works
Before sludge enters the press it is chemically conditioned for dewatering with a liquid polymeric coagulant that helps form stronger floes. After chemical conditioning, a transfer pump drops the sludge to a moving porous belt and distributed all over its operation length. As sludge is conveyed along the belt, the filtrate draining in this zone occurs under gravity force, which takes sludge solids concentration to 5-15% from 0,5-3%. Then the sludge enters the pressing zone, where die sludge is sandwiched between two (2) tensioned belts, by passing those belts through a serpentine of decreasing diameter rolls.
To prevent sludge splashing and extrusion along the belts edges, the pressure onto sludge increases gradually. The dewatering zone can actually bedivided into three (3) zones: gravity zone, which repeats the process before sludge is fed into pressing zone; wedge-shaped preliminary pressing zone, where the solids are prepared for pressure application; and pressure zone, where medium, then high pressure is applied to the conditioned solids. Hie discharged sludge cake can reach variable dry solid content between 18 to 35%.
Finally, the pressed sludge is scraped off the belt and collected in a bin. All filtrate and wash water are captured and transferred back to die front of the waste water system for re-processing.
