
- Home
- Companies
- Decision Makers Ltd.
- Software
- MindSet Detector - Version 2.0 - Water ...

MindSet Detector - Version 2.0 -Water Systems Monitoring Server
MindSet Detector is designed to monitor and detect abnormal behavior in water systems, based on several techniques: "Rare Combination" Alerting The proprietary algorithm classifies historical event data, event frequency, and relevancy as Known, Unknown, Hazard, Maintenance, etc. This enables the system to detect when a new or rare combination of variables occurs and distinguish between false and real alarms.
Trend-Based Alerting
Long-term trend analysis enables the Detector to identify and alert for deterioration of equipment or processes and recommend corrective actions.
Noise-Based Alerting
The patent-pending algorithm detects changes in the variables distribution shape, sending an alert when fluctuations in the noise patterns are recognized.
Rule Engine Alerting
Detects abnormal events based on expert rules. MindSet Detector can run multiple models simultaneously and alert for each one separately.
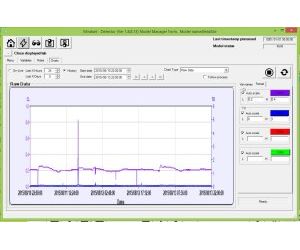
MindSet Detector is built as a server, using Windows services architecture. It can be used as a stand-alone product, or be integrated in any .net system using its API. OPC connectivity enables the integration of Detector with any SCADA.

Based on both public and proprietary machine learning algorithms, Detector builds a mathematical model for each selected unit that describes the relationship between inputs and outputs. No knowledge of mathematical modelling is required - models are generated automatically.
In order to avoid false alarms when your system moves from one state to another, Detector monitors operational changes in process variables.

Communication problems, data with low quality (e.g., fixed values for an over-extended period), operational events (e.g., abnormal pressure or flow), operational changes which generate short-term disturbances to water quality, and true quality water changes.

Adjust for model sensitivity, or set target value for false positives and false negatives.

Classify events as Hazard, Non-hazard, Maintenance, or Instruments Malfunctioning, in order to improve model performance.

The Spatial Model is an EDS module that allows the EDS to detect abnormal water quality measurements across a network. The model utilizes proprietary algorithms for building adaptive thresholds for the water quality measurements across the monitored network.
The main challenge in doing so is adjusting for the flow time of water between stations (water age). With enough data, the Spatial Model is able to estimate the time required for water to flow between network nodes. Thus, it is able to answer the question: "Given this water quality at the water source, what water quality can I expect to see at measurement location X inside the water distribution network?"
Flow time estimation by the Spatial Model is conducted based on the historical data of the water distribution network. Flow time may be estimated for different flow regimes by hours of the day and days of the week. The Spatial Model can thus also be used to validate the results of hydraulic models.
Smart Event Detection
Detect abnormal water quality events on a network scale. Adjust to changing water quality between seasons and time of week/day.
Statistical Estimation of Flow Time
A Statistical Model is used to estimate the correlation between stations across different times.
Fully Incorporated Into EDS
The Spatial Model is an integral part of the EDS, requiring minimal additional installation.
Identifying pending problems in industrial systems is accomplished in many cases by detecting rare events. Detector`s methodology is based on such monitoring of the existence of rare events, i.e. combinations of data that have not seen before. Rare events may be detected both on distance-based or density-based approaches.