- Home
- Companies
- Conifer Systems
- Products
Conifer Systems products
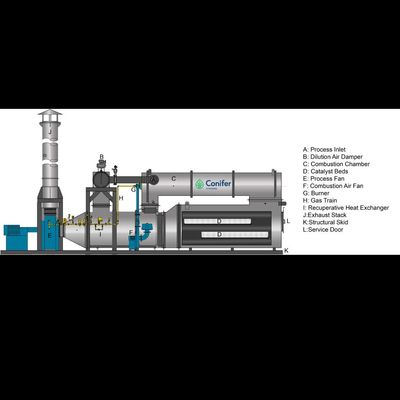
Conifer Systems - Model DTFO - Direct-Fired Thermal Oxidizers
Direct-Fired Thermal Oxidizers (DTFO) destroy emissions that are created through chemical processes found in industrial exhaust streams through the process of combustion. By raising the exhaust stream temperature, the molecules are safely broken down into carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O) and thermal energy.
Conifer Systems - Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer
Regenerative Thermal Oxidizers (RTO) are used to destroy high volumes of emissions that are created through chemical processes, as well as those from industrial exhaust streams. Extremely high heat treats the exhaust of dangerous pollutants and compounds using ceramic media. RTOs are commonly configured in two, three and multi-canister systems to meet any organizations’ needs for ensuring odor and organic material are destroyed. RTOs are a great solution for any process that requires continuous operation.
Conifer Systems - Model Scrubber - Scrubbers
Scrubbers remove dangerous particles from industrial gas streams without burning or using fuel. Scrubbers are ideal for applications that require high temperatures, highly acidic exhaust streams, or harsh chemicals.