

- Home
- Companies
- Focus Laboratories Inc.
- Products
- Focus - Membrane Filtration
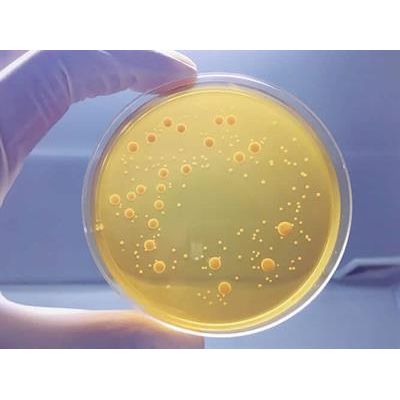
Focus - Membrane Filtration
Sample prepared in diluent as in Pour Plate or Spread plate but the resulting dilution is passed through a 0.22 micron filter. The filter is removed and placed on the surface of nutrient agar plates, allowing microbes to growth to visible colony forming units. Membrane filtration is recommended with chemical neutralization of antimicrobial agents is not possible, such as with antibiotics. The filtration physically separates the antimicrobial from the contaminant, leaving the microbe on the surface of the filter for further culturing. It is also useful when the limit of detection must be
Most Probable Number
Most Probable Number (MPN) is less precise and accurate then Plate Count of Membrane Filtration Method, but can be advantageous when looking for limits of detection that are <10 and if adding certain inhibitory compounds to count specific types of bioburden. An example of the latter would be counting coliforms by MPN using Lauryl Sulfate Broth. Essentially, dilutions of product, or straight product, are placed in a series of broth tubes. These broth tubes are incubated for a period of time and then inspected for turbidity which is taken as a sign of growth. The count of tube dilutions with growth is then compared to a statistical table to obtain “the most probable number” per mL.
Microbial Suitability
Any microbial enumeration test must be validated to show that any organisms in the product can actually be cultured. As mentioned above, antimicrobial properties of the product may inhibit the growth of a microbe in agar to become a visible colony forming unit. Validation or “suitability” is accomplished by inoculating plated product with low levels (<100 cfu) of test species and demonstrating equivalence to recovery of that organism in the absence of the product. Microbial enumeration methods are considered suitable if product results are 50 – 200% of control results.
Microbes used to demonstrate suitability of the dilution and enrichment method are the same organisms used to demonstrate the growth promotion ability of media used in the test.
